【英文】【原创】参照“使用数字化实现共产主义”的思路,探讨构建数字生态
ORIGINAL:DRAWING ON THE CONCEPT OF 'USING DIGITAL TO REALIZE COMMUNISM', EXPLORES THE CONSTRUCTION OF A DIGITAL ECOSYSTEM
UNRELATED TO POLITICS, EXPLORING AND DISCOVERING, EXCHANGING AND DISCUSSING.

Author: Nick Lee (Li Sheng Guo) of HS Future, March 23rd, 2023
E-mail: nick@hszs.org.cn
Note: If you need to reprint, quote, or use any part or all of the text, content, and method ideas in this paper, you must first contact the author to obtain written authorization before reprinting, quoting, or using them.
I. Introduction
A. Background, Purpose, and Significance of the Study
1.The Background of the Study
The background of this research paper lies in the complex issues and challenges faced by the world today, such as globalization, population growth, ecological destruction, international instability in relations, economic downturns, etc. These problems have put unprecedented pressure on the development of human society, and have also exposed many issues and limitations in traditional economic and social forms, including unfair resource allocation, widening wealth gap, distorted values, lack of social integrity, spiritual impoverishment, environmental degradation, etc.
The rapid development of digital technology provides new ideas and means to address these problems. The application of digitization can bring about more efficient, fair, and sustainable ways of economic and social development, break through the bottlenecks of existing economic and social forms and productivity development, and promote the progress of human society. Therefore, this research paper will focus on exploring how to use digital means to construct a digital ecosystem that supports the digital economy, in order to achieve more efficient, fair, and sustainable social and economic development.
By referencing the concept of communism, the comparison and analogy between the digital ecosystem and communism can help better understand the concept and significance of the digital ecosystem. Thus, the research background of this paper is the development of digital technology and the current problems and challenges faced by the world, with the aim of exploring how to construct a digital ecosystem that supports the digital economy through digital means.
2.The Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this thesis is to explore the use of digital means to achieve the ideals of communism and propose ideas and methods for building a digital ecosystem. This thesis aims to analyze and study the soft infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, and explore how digital technology can be utilized to create an ecosystem for the digital economy, providing specific ideas and recommendations to achieve this goal. Through this research, the aim is to promote in-depth exploration and communication among academia and various sectors of society regarding the relationship between digitization and ecosystem, and provide more ideas and methods for the realization of a truly digital ecosystem, further advancing human society's development.
3.The Significance of the Study
The significance of this research lies in:
a) Exploration of Communist Theory and Practice
Communism is an ideal social system, but in past practices, it has not been fully realized due to various reasons. Through the research in this paper, new ideas and approaches can be provided for the realization of communism.
b) Promoting Deep Integration of Digitization and Ecological Systems
The digital ecological system is a comprehensive system that requires deep integration in multiple areas such as digital technology, organizational forms, ecological conservation, and industrial upgrading. Through the exploration of using digital means to realize the concept of communism, this paper provides a new approach and method that can promote the deep integration of digitization and ecological systems, providing theoretical support and practical pathways for achieving sustainable development and green economy.
c) Promoting the Integration of Digitization and Social Governance Development
Digitization has become an important driving force for modern social development, as well as a crucial tool and technical support for modern governance. The research in this paper can explore the path of integrating digitization and social development, thereby promoting the healthy and sustainable development of society in the digital era.
d) Promoting High-Quality Development of the Digital Economy
The digital economy is a major trend in global economic development, and the digital ecological system is the key to high-quality development of the digital economy. The research in this paper aims to explore the construction of the digital ecological system, with a focus on the application of digital technologies. By establishing a digitalized ecological system, it can improve the efficiency, fairness, and sustainability of the digital economy, and promote its high-quality development.
e) Highlighting the Importance of Establishing a Digital Ecological System
Digital technologies have profoundly changed our lives and economic forms, providing new avenues for realizing communism. Establishing a digital ecological system can not only promote the development of the digital economy, but also provide digital means and support for achieving communism. This is of significant and crucial importance.
The application of digital means can promote the fair distribution of social resources, collaborative sharing of labor, establishment of social credit, protection of privacy and data security of stakeholders, and the realization of scientific governance and industry regulation, among others. The digital ecological system can promote resource sharing, provide necessary conditions for accessible information sharing and equal competition, and provide technological support for building a more equitable society.
f) Conclusions
In conclusion, the significance of this paper's research lies in providing new ideas and methods for the construction of a digital ecological system, promoting the deep integration of digitization with ecological systems and social governance development, and advancing the high-quality development of the digital economy. It has important practical significance and theoretical value for promoting the coordinated development of the economy, society, and environment.
B. Theory and Historical Practice of Communism
1.Theory of Communism
Communism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for the establishment of a classless, stateless, and propertyless social system, where the means of production are collectively owned and managed by the people, to meet the material and cultural needs of the population, eliminate social inequality and exploitation, and achieve common prosperity and ultimately a communist society.
2.Goals of Communism
g) Abolition of private ownership and exploitation
Communism advocates for the abolition of private ownership and the establishment of social ownership. This includes all means of production such as land, factories, machinery, transportation, etc. Abolishing private ownership can eliminate the exploitation between individuals and achieve true equality among humanity.
h) Establishing a Classless Society
Communism advocates for the elimination of class distinctions and the establishment of a classless society. In a communist society, all individuals are equal, and there are no class conflicts or oppression. Everyone can freely express their talents and creativity.
i) Achieving Common Prosperity
Communism advocates for the realization of common prosperity for all. In a communist society, everyone can access basic livelihood security and public services such as food, housing, education, healthcare, etc. Additionally, communism promotes the fair distribution of the fruits of labor based on work and need, fulfilling the material and cultural needs of every individual.
j) Abolishing State and Political Power
Communism advocates for the abolition of the state and political power. In a communist society, there is no longer a need for government or other forms of ruling institutions, as all matters are decided democratically and managed collectively. This can eliminate the limitations and control of the state and political power over the people.
k) Promoting Human Freedom and Individual Development
Communism advocates for the promotion of human freedom and individual development. In a communist society, every individual can fully express their talents and potential, pursue their own ideals and goals, while also contributing to society with their own contributions.
3.Historical Evolution of Communist Theory
The history of communism can be traced back to the mid-19th century, when some socialist thinkers began to criticize capitalism and put forward new ideas for alternative social systems. The following are the main stages in the historical evolution of communism:
a) Early Socialism
In the mid-19th century, some socialist thinkers such as Saint-Simon, Fourier, and Owen in France began to criticize the capitalist system and proposed the establishment of a more fair and equal social system. These early socialists advocated for "utopian socialism" and proposed small-scale social experiments such as social communities or cooperatives.
b) Marxism
In the 1860s, the German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels began to collaborate in England and systematically developed the theory of Marxism. Marxism believes that capitalism is an oppressive and exploitative system, and only through the revolution of the working class can capitalism be overthrown and the establishment of a classless communist society be achieved to achieve the thorough emancipation of humanity.
c) Russian Revolution
In 1917, the October Revolution took place in Russia, where the Bolshevik Party led the workers, peasants, and soldiers to overthrow the Tsarist government and establish the world's first socialist state - the Soviet Union. Leaders such as Lenin and Stalin implemented a series of socialist and communist policies and measures in the Soviet Union, including nationalization, collectivization, and industrialization, in an attempt to build a classless society and a socialist economic system.
d) Global Communist Movement
The establishment and development of the Soviet Union inspired communist movements worldwide. In the mid-20th century, many countries saw the rise of communist regimes, such as China, North Korea, Cuba, Vietnam, and others. These countries attempted to establish communist social systems and implemented various economic, political, and cultural socialist reforms in different historical contexts.
e) Decline of Communism
At the end of the 20th century, the Soviet Union collapsed, and communist regimes in Eastern Europe also collapsed one after another. Due to various reasons such as planned economy, political system, and cultural system, these countries faced enormous challenges and difficulties in their economic, political, and social systems. Criticisms of communism reached their peak worldwide, and many countries began to transition to market economy and democratic politics.
f) Transition of Communism
Faced with external pressures and internal challenges, some countries have started to reform and transition from communism. For example, China began implementing the policy of reform and opening up in the early 1980s, gradually relaxing the planned economy, introducing market mechanisms, and promoting political and social reforms. Cuba, Vietnam, and other countries have also carried out varying degrees of reforms and adjustments to communism.
g) Conclusion
Although communism has lost its former influence and attractiveness worldwide, its impact on contemporary politics, economy, and culture still exists. For example, some ideas, methods, and strategies from communist theories and practices are still relevant and informative in today's world. Moreover, the historical experiences of communism provide important reflections and insights for understanding the complexity and diversity of contemporary society and politics.
4.Historical Practices of Communism
a) Paris Commune
The Paris Commune was the first attempt in the history of communism. Within three months in 1871, Parisian citizens spontaneously formed a government, attempting to establish a labor-centered social system and empower workers and peasants. However, they ultimately failed due to military intervention by the French government.
b) Spanish Revolution
Between 1936 and 1939, the Spanish people attempted to establish an anarchist society. They created collectives composed of workers and peasants, aiming to achieve decentralization, democracy, and fairness. However, this revolution was suppressed by the fascist regime during the Spanish Civil War.
c) Hungarian Revolution of 1956
In 1956, Hungarian students and workers rose up to establish a democratic, socialist social system. They overthrew the Communist Party regime, attempting to establish a labor-based social system. However, the Soviet army entered Hungary and suppressed the revolution.
d) People's Communes as a Form of Collective Economy
People's Communes were a form of collective production organization implemented in mainland China in the 1960s, with the goal of realizing the public ownership of means of production and the distribution according to labor. Under this system, the means of production and labor force in rural areas were incorporated into the collective ownership and centralized allocation of the communes. Individual farmers could only obtain corresponding living supplies and services from the commune, and receive income distribution according to their labor contribution. This system was an attempt at communist practice, aiming to achieve the socialization of wealth, common prosperity for the people, and equal distribution of labor. However, these systems did not achieve the expected results in practice.
C. How Digital Means Facilitate the Realization of Communism
Digital means can facilitate the realization of communism in multiple ways:
1.Resource allocation and wealth disparity
Digital means can reduce resource waste and abuse, and achieve fair distribution of resources through universal, fair, and transparent resource allocation mechanisms. For example, through digital financial systems and payment platforms, financial services can be inclusive and accessible to more people, reducing wealth disparity. Additionally, digital means can achieve fair distribution of social resources through digital social security and welfare systems, helping the impoverished population to lift themselves out of poverty and promoting common prosperity in society.
2.Ecological environment protection
Digital means can enable fine management and effective protection of the ecological environment through intelligent environmental monitoring, data analysis, and prediction. For example, through digital big data and artificial intelligence technologies, real-time monitoring and analysis of environmental indicators such as air quality, water quality, and soil can be conducted, enabling early warning of environmental pollution and ecological damage, and taking corresponding measures for restoration and protection. Digital means can also promote the development and utilization of sustainable energy, drive low-carbon economy and green development, and achieve a virtuous cycle of economy and ecological environment.
3.Social Credit and Values
Digital means can enhance the transmission and practice of social credit and values through information management and data sharing. For example, through digital credit systems and social evaluation mechanisms, individuals and enterprises can be comprehensively monitored and evaluated, and integrity incentives and dishonesty penalties can be established to promote adherence to the principles of honesty and trustworthiness in all aspects of society. Digital means can also transmit positive energy and positive values through digital media and social networks, promoting social harmony, inclusiveness, and win-win outcomes.
4.Education and Spiritual Civilization Construction
Digital means can promote the popularization of education and the sharing of high-quality resources through online education, digital cultural inheritance, and other means. For example, through digital education platforms and online learning resources, more people can access high-quality educational resources, narrow the education gap, and improve the quality and skills of the general public. Digital means can also promote the protection and inheritance of traditional culture through digital cultural inheritance and innovation, cultivate people's spiritual world and civilizational literacy, promote the construction of spiritual civilization in society, and cultivate the core values of communism.
5.Social Organizations and Participation
Digital means can promote the extensive development of social organizations and participation through social networks, online platforms, and other means. For example, through digital social media and online communities, people's interactions and communications can be promoted, forming a more extensive social network, and promoting the diversification and broadening of social organizations and social participation. Digital means can also achieve effective links between public participation, social governance, and democratic decision-making through online democratic and participation platforms, promoting transparency and democracy in social decision-making, enhancing the awareness and sense of participation of the general public in the cause of communism.
6.Production and distribution methods
Digital means can optimize and upgrade production and distribution methods through digital production, logistics, distribution, and other methods. For example, through digital supply chain management and intelligent logistics, production efficiency and resource utilization can be improved, production costs can be reduced, and production processes can be made intelligent and sustainable. Digital means can also optimize the allocation and distribution of resources, information, and value through digital economy and platform economy, promoting shared economy and common prosperity in society.
7.Government governance and public services
Digital means can improve the efficiency and quality of government governance and public services through e-government and digital government. For example, through digital government service platforms, convenient and efficient government services can be provided, administrative costs can be reduced, and interaction and trust between the government and the people can be enhanced. Digital means can also integrate and analyze government data through big data and artificial intelligence technologies, support scientific formulation of government decisions and public policies, and promote the modernization and democratization of government governance.
8.Conclusion
In general, digital means can promote the realization of communism through providing inclusive, fair, and transparent resource allocation mechanisms, ecological and environmental protection, improving social integrity and values, promoting education and spiritual civilization, promoting social organizations and participation, optimizing production and distribution methods, and enhancing government governance and public services. However, digital means also face challenges such as data privacy, information security, and digital divide, which need to be fully considered and addressed to ensure that the application of digital means is in line with the core principles and goals of communism and truly benefits the people.
II.Integration of Traditional Communist Theory with Digital Means
A. Limitations and Drawbacks of Communist Theory in Historical Practice
The practice of communism has demonstrated the aspirations and pursuit of social fairness, justice, and common prosperity for the majority of people. However, it has also faced failures and shortcomings that cannot be overlooked. These are primarily reflected in the following areas:
1.Weakness in organizational structure
The implementation of communism requires the socialization of means of production and fair distribution, which entails significant adjustments to existing class and interest group relations. These groups, who hold economic and political power and may even possess substantial military forces, pose direct threats to the practice of communism. As a result, communism has faced various pressures, interferences, and obstacles during its implementation, particularly during the Cold War period when Western countries like the United States resorted to the use of force, political sanctions, and severe crackdowns to suppress and undermine communist attempts, resulting in failures.
2.Neglect or inability to balance human nature issues
Communist theory emphasizes class struggle and exploitation as inevitable phenomena in the development of human society but overlooks the selfish and utilitarian factors in human nature. It fails to effectively address fundamental issues such as integrity, corruption, opportunism, self-interest, and favoritism, and also neglects the needs of individual freedom and dignity. As a result, it is unable to fully unleash the creativity and vitality of individuals.
3.Insufficient social infrastructure and productive forces
In the practice of communism, due to inadequate infrastructure and low level of productivity, there is often low production efficiency, which fails to meet the basic needs of the people, resulting in social conflicts and grievances.
4.Issues with political systems
Communism often faces problems such as "dictatorship" and "authoritarianism" in practice, resulting in a rigid political system and lack of supervision, leading to corruption, oppression, and violation of people's rights and democratic liberties.
5.Cultural and educational issues
Communism tends to neglect the importance of culture, education, and ideological diversity in practice, emphasizing collectivism and internationalism while overlooking national and regional differences, resulting in cultural homogenization and ideological stagnation.
6.Issues with production relations and means of production
There are problems in the elimination of private ownership of means of production and the establishment of public ownership, resulting in unstable production relations and declining productivity. In addition, planned economy often suffers from inefficiency, resource waste, and lack of market competition. In many practices of communism, economic planning and management are inadequate, lacking sufficient market mechanisms to adjust production and distribution. This results in low economic efficiency, resource waste, scarcity, as well as inadequate and low-quality supply of goods.
7.Conclusion
In summary, the limitations and drawbacks of communism in practice cannot be denied, but it does not mean that the ideals and pursuit of communism are unattainable. In the face of global challenges such as resource and environmental issues, wealth disparity, and social injustice, we still need to reflect on and explore better social organization and development paths, which require innovation and development based on the ideals and practice of communism.
B. Challenges of Using Digital Means to Promote Communism
If we want to use digital technology to achieve communism, we may face the following challenges:
How can digital technology be used to eliminate private ownership? Is it necessary to establish a global public ownership platform? Who will manage and supervise this platform? How can the fairness and reliability of the platform be ensured?
How can digital technology be used to distribute production materials and products? Is it necessary to establish an intelligent demand and supply matching system? Who will determine the standards and priorities of demand and supply? How can the flexibility and adaptability of the system be ensured?
How can digital technology be used to promote collective production? Is it necessary to establish an open collaboration network? Who will participate in and contribute to this network? How can the efficiency and innovation of the network be ensured?
How can digital technology be used to achieve a classless society? Is it necessary to establish an equal social evaluation mechanism? Who will evaluate and reward members of society? How can the fairness and incentivization of the mechanism be ensured?
How can digital technology be used to abolish currency and nation states? Is it necessary to establish a currency-free exchange system? Who will maintain and operate this system? How can the stability and security of the system be ensured?
How can digital technology be used to fulfill the needs of human self-development? Is it necessary to establish a diverse cultural and educational platform? Who will provide and enjoy this platform? How can the diversity and freedom of the platform be ensured?
The above are just some preliminary ideas, which may not be correct or complete. However, overall, there are many challenges in using digital means to promote the realization of communism.
C. Ways to Promote the Realization of Communism Using Digital Means
There are several ways in which digital means can promote the realization of communism:
1.Achieving resource sharing and optimized allocation
Digital technology can help collect, process, analyze, and share information about various resources, including the efficient coordination and optimized allocation of production factors through the full life-cycle management of data elements such as collection, analysis, application, and sharing. Digital tools can make the flow of production factors more efficient, thereby achieving globally optimal production factor allocation in a communist production mode, improving resource utilization and economic efficiency. Digitizing and sharing forms of ownership. By using digital technology, rigid constraints under existing property rights systems can be broken, promoting the sharing and circulation of production factors, achieving optimized allocation and rational use of resources, eliminating waste and injustice in society, and promoting resource sharing and common prosperity.
2.Optimizing production relations
Using digital technology to improve the contradiction between productivity and production relations. Digital tools can achieve deep integration of industrialization, informatization, and intelligence, optimizing production relations through intelligent production, collaborative manufacturing, and personalized production, and realizing the high-efficiency and high-quality development of productivity, providing strong guarantees for the communist production mode.
3.Promoting productivity development and improving production efficiency
Digital technology can enhance productivity, such as automated production lines, artificial intelligence technology, etc., thereby increasing product output and quality, reducing production costs and labor costs, and improving production efficiency.
4.Achieving information transparency and democratic decision-making
Digital technology can achieve information transparency, making it convenient for people to access various information and participate in the decision-making process of social affairs, promoting democratic decision-making and democratic governance, and improving social fairness and justice. For example, through the distributed ledger and consensus mechanism of blockchain, information transparency and democratic decision-making can be achieved while protecting privacy and data security.
5.Building a digital sharing economy
Digital technology can promote the construction of a digital sharing economy, which involves building sharing platforms through digital technology to facilitate resource sharing and exchange among people, thereby improving the efficiency of resource utilization and promoting the common development of the social economy.
6.Improving the level of social governance
Digital technology can enhance the efficiency and level of social governance, such as digital government affairs, smart cities, intelligent regulation, and AI-assisted governance, promoting social stability and sustainable development.
7.Conclusion
III. The similarities between digital ecosystem and communism are as follows
A. Goals and Vision
There are many similarities between digital ecosystem and communism in terms of goals and vision, including but not limited to:
1.Emphasis on public interest
Both digital ecosystem and communism prioritize public interest. The digital ecosystem aims to provide comprehensive and wide-ranging digital services to meet people's various needs, including information, entertainment, communication, and learning. Communism, on the other hand, aims to eliminate wealth disparity, promote fairness and justice, and emphasize the development of individuals and the overall development of society.
2.Emphasis on sharing and cooperation
Both digital ecosystem and communism value sharing and cooperation. The digital ecosystem aims to promote knowledge sharing and innovation cooperation in the digital world, enhancing the exchange and sharing of information and knowledge through an open and interactive digital ecosystem. Communism, on the other hand, emphasizes the spirit of cooperation and socialist collectivism in a communist society, achieving the public ownership and sharing of social resources and economic wealth.
3.Advocacy for openness and inclusivity
Both digital ecosystem and communism advocate for openness and inclusivity. The digital ecosystem emphasizes openness and inclusivity in the digital economy, encouraging communication and interaction from multiple perspectives, and promoting the democratization and globalization of the digital economy. Communism advocates for an open, free, and equal social environment that allows everyone to fully leverage their talents and potentials to achieve self-worth.
4.Emphasis on technological innovation and development
Both digital ecosystem and communism emphasize technological innovation and development. The digital ecosystem requires continuous technological innovation and development to drive the advancement and progress of the digital economy. Communism also requires continuous technological progress and development to improve social productivity and people's living standards.
5.Focus on ecological protection and sustainable development
Both digital ecosystem and communism value ecological protection and sustainable development. The digital ecosystem needs to consider the ecological environment and resource utilization of the digital economy, avoiding resource waste, environmental pollution, digital pollution, and exacerbation of the digital divide. Communism needs to focus on sustainable development, achieving economic, social, and environmental sustainability to meet current and future needs.
6.Advocacy for people's democracy and participation
Both the digital ecosystem and communism advocate for people's democracy and participation. In the digital ecosystem, all stakeholders participate in the construction and development of the digital economy, and through consensus mechanisms and collaborative governance, promote democratization and popularization of the digital economy. Communism emphasizes people's democracy and participation, advocating for people to participate in social and political decision-making through universal suffrage, open debates, and other means, promoting democratization and development of the state and society.
7.Emphasis on common development and mutual assistance
Both the digital ecosystem and communism emphasize common development and mutual assistance. The digital ecosystem requires collaborative efforts and cooperation among all parties to promote the advancement and development of the digital economy. Communism emphasizes mutual assistance and support, aiming to achieve common development and prosperity.
8.Emphasis on comprehensive human development
Both the digital ecosystem and communism emphasize comprehensive human development. The digital ecosystem needs to provide comprehensive digital services to meet the diverse needs of people and promote their holistic development. Communism emphasizes comprehensive human development and freedom, providing equal opportunities and conditions for every individual to realize the unity of personal and social values.
9.Conclusion
In summary, the digital ecosystem and communism share many similarities in terms of goals, content, and theories. Through these similarities, they can learn from each other and mutually promote, exploring paths and models that are more suitable for the development of society in the present and future.
B. Issues and Challenges
The digital ecosystem and communism share many similarities in terms of issues and challenges, including but not limited to:
1.The issue of equality and fair distribution
Both the digital ecosystem and communism need to address the issue of equality and fair distribution. The digital ecosystem needs to tackle the problem of uneven distribution of digital resources and the digital divide, ensuring that every participant can access digital services and resources on an equal basis. Communism, on the other hand, needs to address the wealth gap and achieve public ownership and equitable distribution of wealth and resources, aiming for common prosperity.
2.Issues of property security and privacy protection
Both the digital ecosystem and communism need to address issues of property security and privacy protection. The digital ecosystem needs to address problems such as data leaks, data misuse, and cyber attacks to safeguard the ownership, security, and privacy of data elements for all participants. Communism needs to prevent personal rights from being violated, information from being abused, and safeguard individual rights and privacy, including property rights of the people.
3.Governance and regulatory issues
Both the digital ecosystem and communism need to address governance and regulatory issues. The digital ecosystem needs to establish effective governance and regulatory mechanisms to ensure the order and stability of the digital economy, as well as the ability to evolve continuously. Communism needs to address the issues of state machinery management and bureaucratic practices to ensure fairness and transparency in government management and regulation.
4.Issues of education and training
Both the digital ecosystem and communism need to address issues of education and training. The digital ecosystem needs to enhance the digital literacy and skills of participants to adapt to the development and changes in the digital economy era. Communism needs to provide comprehensive education and training for the people to improve their qualities and capabilities.
5.Social and cultural issues
Both the digital ecosystem and communism need to address social and cultural issues. The digital ecosystem needs to consider the integration and conflicts of technology and culture in the digital economy to promote the development of digital society and culture. Communism needs to address the diversity and differences in society and culture to achieve social harmony and cultural exchange.
6.Conclusion
The digital ecosystem and communism share similar unresolved issues that involve the progress and development of human society, requiring collective efforts and solutions at a global level. In the process of addressing these issues, the digital ecosystem and communism can learn from and reference each other, mutually promote and develop together.
C. Insights and References from Communism for Building the Digital Ecosystem
The methods and means of achieving communism can provide valuable insights and references for building a digital ecosystem. The central idea of communism is to eliminate private ownership and achieve public ownership and sharing of resources, while pursuing ecological balance and sustainable development. The digital ecosystem also shares similar goals, such as digitization, networking, and intelligence, which can enable information and resource sharing, improve production efficiency, and environmental protection. The following are detailed explanations:
Firstly, communism advocates public ownership and sharing of resources, and the digital ecosystem also promotes information and resource sharing. Communism advocates the elimination of private ownership and the socialization of means of production, achieving public ownership and sharing of resources. The characteristics of digitization, networking, and intelligence in the digital ecosystem contribute to the public ownership, sharing, and distribution of resources in communism. The establishment of a digital ecosystem is based on data element sharing and interconnection, promoting innovation and collaboration through open data and resource sharing.
Secondly, communism pursues ecological balance and environmental protection, and the digital ecosystem also promotes concepts such as circular economy, sharing economy, and green ecology. Communism attaches great importance to environmental and ecological protection, which contributes to the sustainable development and ecological civilization in communism. The concepts and practices of the digital ecosystem, such as circular economy, sharing economy, and green ecology, provide ideas and methods. The digital ecosystem incorporates concepts and technologies such as intelligent manufacturing, industrial internet, etc., which contribute to efficient production and technological development in communism. Concepts and technologies such as digital economy, artificial intelligence, blockchain, etc., in the digital ecosystem can also be applied to social management and governance to improve the efficiency and fairness of social management. Digital technologies can be applied to social management and governance in communism, such as digitized government affairs, digital public services, and smart city construction based on big data and artificial intelligence, which can improve the efficiency and fairness of social management.
Lastly, the ideas and methods of achieving communism provide a sustainable development and social governance approach for building the digital ecosystem. Communism aims to achieve comprehensive social progress, and the characteristics of digitization, networking, and intelligence in the digital ecosystem provide more specific, efficient, and sustainable methods for achieving communism. The concepts and technologies in the digital ecosystem, such as information sharing, resource sharing, circular economy, sharing economy, green ecology, digital economy, artificial intelligence, blockchain, etc., contribute to various aspects of the digital economy, including resource sharing, ecological balance, sustainable development, and technological progress. Concepts and technologies such as intelligent manufacturing, industrial internet, etc., in the digital ecosystem also contribute to efficient production and technological development in the digital economy.
In conclusion, communist ideas and methods provide valuable insights and references for building a digital ecosystem, and the concepts and practices in the digital ecosystem provide sustainable development and technological progress approaches for achieving communism.
IV. Concepts and Components of the Digital Ecosystem
A. Concepts and Characteristics of the Digital Ecosystem
The digital ecosystem is a form of economic development based on digital means, which establishes a corresponding digital ecological economy through the application and innovation of digital technologies. It promotes optimal allocation of resources and productivity enhancement, aiming to achieve sustainable economic and social development. The digital ecosystem emphasizes the importance of digital means in the economic system and the role of the digital ecosystem in promoting sustainable economic development. It also highlights the indispensability of digital technology application and innovation in economic development. It is a fundamental solution to social integrity issues, aiming to achieve the goals of "publicness" and "commonness" by building a fair, just, transparent, collaborative, shared, symbiotic, win-win, and consensus-based digital ecological economy. It is a new form of economy that surpasses traditional digital platform economy in terms of breadth, relying on the consensus and governance mechanisms of ecological economy, and can encompass multiple traditional economic forms, suitable for various industries and sectors, serving as a collective platform for empowering successful digital transformation of traditional economic forms in society and business. It possesses the characteristics of being inclusive to all citizens and global in scope.
B. Elements of the Digital Ecosystem
1.Digital Technology and Infrastructure
Digital technology is the foundation of the digital ecosystem, including but not limited to artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, cloud computing, communication technology, IoT, and other emerging digital technologies that provide technical support for the operation of the digital ecosystem.
Digital infrastructure is built on the basis of digital technology, including hardware infrastructure and software infrastructure. Hardware infrastructure includes network communication infrastructure, data center infrastructure, service node infrastructure, and other aspects that provide necessary support for the operation of the digital ecosystem. Software infrastructure includes digital identity networks, consensus-based governance networks, social (community) networks, financial transaction and payment networks, cross-platform API service networks, open-source contribution networks, data element circulation networks, big data AI service networks, and human-computer interaction infrastructure.
2.Data Element Resources
Data element resources are the core elements of the digital ecosystem, which can be divided into digital information and digital assets according to their attributes, and public data elements, industrial data elements, entity data elements, and personal data elements according to their scope. The lifecycle of data element resources in the ecosystem includes collection, rights confirmation, storage, processing, circulation, traceability, quality evaluation, value assessment, transaction, sharing, application monetization, and revenue distribution. The sharing and openness of data element resources are the cornerstone of the development of the digital ecosystem.
3.Participating Entities
Participating entities, including individuals, organizations, enterprises, government agencies, etc., are the very reason why the digital ecosystem can be called an ecosystem, and various activities within the ecosystem can take place. The interdependence and interconnection among various participating entities collectively form the framework and foundation of the digital ecosystem, providing support and guarantee for the rapid development of the digital economy and digital society.
Individuals, organizations, enterprises, government agencies, and other participating entities play different roles in the digital ecosystem. Individuals contribute to the development of the digital economy and digital society by participating in the digital ecosystem through the use of various digital technologies and services. Organizations contribute to the development of the digital economy and digital society through the composition of various industry chains, value chains, and service chains, as well as the interconnections and interdependencies among various links. Enterprises promote the rapid development of the digital ecosystem through innovation, entrepreneurship, and new product research and development. Government agencies provide support and guarantee for the rapid development of the digital ecosystem through policies, regulations, industrial planning, financial support, supervision, and services.
The interactions and interdependencies among these participating entities collectively ensure the coordination and balanced development of various elements within the digital ecosystem. Only in this way can the rapid development of the digital economy and digital society be achieved.
4.Consensus Organizations
Consensus organizations refer to a form of organization and mechanism formed through negotiation, cooperation, and other means among various participating entities in the digital ecosystem. The formation of consensus organizations can ensure that the digital ecosystem operates according to the intended goals and continuously improves and optimizes itself.
In the digital ecosystem, there are many other forms of consensus organizations, such as industry alliances in the digital economy and community organizations in the digital society. These consensus organizations promote interaction and communication among various participating entities within the digital ecosystem through negotiation, cooperation, and other means, and drive the rapid development of the digital economy and digital society.
5.Responsibility and Contribution Sharing Mechanism
In the digital ecosystem, cooperation and collaboration among all participating entities should be based on a mechanism that ensures responsibility and contribution sharing. The responsibility and contribution sharing mechanism refers to the concept that all participating entities in the digital ecosystem should assume corresponding responsibilities and obligations, and receive rewards and benefits based on their contributions. This mechanism ensures fairness and equity among the participating entities within the digital ecosystem, avoids unfair competition and resource waste, and serves as a fundamental guarantee for achieving distribution based on labor and common prosperity.
6.Public Service Resources
Public services are an important guarantee for the development of the digital ecosystem, including various facilities, platforms, and projects that provide convenience and support for the development of the digital ecosystem. Public services can improve the efficiency and quality of the digital ecosystem, provide convenience and support for various economic activities and social services within the digital ecosystem. Public services can promote innovation and transformation within the digital ecosystem by providing platforms and resources for innovation, entrepreneurship, and new product development. Public services can enhance the sustainability and resilience of the digital ecosystem by providing support and guarantee for risk response and crisis management within the digital ecosystem. Public services can also enhance the fairness and inclusiveness of the digital ecosystem by providing open, fair, and equitable opportunities and conditions for various stakeholders. Public resources are commonly owned by all participating entities.
7.Industrial Ecosystem
The industrial ecosystem is an important component of the digital ecosystem, representing the specific expression and basic unit of the digital ecosystem at the industrial application level, and belongs to a sub-ecosystem. It includes various industrial chains, value chains, and service chains, as well as the interrelated and interdependent relationships among different segments. The industrial ecosystem can promote the rapid development of the digital economy and digital society. It can enhance the innovation capability of the digital economy and digital society. It can also enhance the competitiveness of the digital economy and digital society. This industrial ecosystem can drive the development of the digital economy towards higher levels and broader fields.
8.Policy Support
Policy support is a crucial guarantee for the development of the digital ecosystem and an essential element. It includes various policies, regulations, industry plans, financial support, and government services, which provide support and protection for the rapid development of the digital ecosystem.
The main roles of policy support are as follows:
Firstly, policy support can promote the rapid development of the digital economy and digital society. The government provides guarantees and support for the rapid development of the digital economy and digital society through the formulation of various policies, regulations, and industry plans. For example, the government can implement tax incentives policies to encourage investment in the digital economy; can introduce financial support policies to provide financing support for the digital economy, etc.
Secondly, policy support can enhance the innovation capabilities of the digital economy and digital society. The government provides guarantees and support for innovation in the digital economy and digital society through the formulation of various policies, regulations, and industry plans. For example, the government can implement intellectual property protection policies to encourage technological innovation by enterprises; can introduce policies for talent introduction to attract more outstanding talents to participate in the digital economy.
Finally, policy support can enhance the competitiveness of the digital economy and digital society. The government provides guarantees and support for the competitiveness of the digital economy and digital society through the formulation of various policies, regulations, and industry plans. For example, the government can implement market access policies to promote market competition; can introduce international cooperation policies to expand international markets, etc.
9.Optimization of Production Relations
Production relations are a crucial element in the development of a digital ecosystem. From a business perspective, it involves optimizing the traditional one-sided, pipeline relationship between businesses, platforms, and consumers into a network of equal and mutually beneficial relationships.
In a digital ecosystem, production relations are diverse. Different participants have different production relations within the digital ecosystem. Production relations in a digital ecosystem are characterized by equality, where all participants are on an equal footing. Production relations in a digital ecosystem are characterized by mutual dependence, mutual promotion, and harmonious coexistence among all participants.
In a digital ecosystem, technological advancements drive changes in productivity, and production relations need to adapt to these changes, forming a two-way shaping relationship. Building a new type of production relations that are suitable for the digital era and promoting the rapid development of productivity in the digital economy is an important path towards building a modern economic system and promoting high-quality development of the digital economy.
10.Enhancement of Ownership Forms
The enhancement of ownership forms is a significant driving force for the development of a digital ecosystem. It includes reforms in property rights systems and changes in ownership forms, providing guarantees for the sustainable development of the digital ecosystem. Changes in ownership forms mainly refer to the integration and development of public ownership and non-public ownership economies, achieving the co-development and prosperity of multiple ownership forms. In the digital ecosystem, the integration, coordination, and resource integration and allocation between public and non-public ownership economies will further deepen.
It is necessary to establish and improve the property rights system in the digital ecosystem, clarifying the rights and obligations of various parties in terms of data resources, technological achievements, product services, etc., and protecting the legitimate rights and interests of all parties. Establishing and improving the transaction mechanism in the digital ecosystem, promoting market-based transactions of data resources, technological achievements, product services, etc., and facilitating mutually beneficial exchanges among all parties. Establishing and improving the collaboration mechanism in the digital ecosystem, promoting collaborative construction among all parties in terms of data resources, technological achievements, product services, etc., and facilitating the common development of all parties.
11.Harmonious And Symbiotic Environment
The harmonious and symbiotic environment, also known as the "three publics" and "six co-'s" digital ecological system, refers to a system in the digital era that is based on the principles of fairness, justice, and transparency, with the goals of co-construction, co-sharing, co-living, co-winning, co-consensus, and co-governance. This system aims to integrate digital technology with the real economy, ensuring data security, circulation, and value creation, while promoting social integrity and fair transactions in the socio-economic ecosystem of the digital era.
12.Conclusion
In summary, these elements are interconnected and interact with each other, collectively forming the framework and foundation of the digital ecological system, providing support and guarantee for the rapid development of digital economy and digital society.
C. Basic Principles and Operational Mechanisms of Digital Ecological System
The digital ecological system is an ecosystem based on digital technology and information development, which connects and manages various aspects of human society in a digitalized manner.
1.Basic Principles
a) Openness
The digital ecological system should be based on an open attitude and an open architecture, fully leveraging the openness and interoperability of digital technologies, strengthening interoperability and connectivity among different digital technologies, encouraging communication, collaboration, and synergistic development among different entities in the digital economy, to promote the development and innovation of the digital economy.
b) Fairness
The digital ecological system should follow the principle of fairness, conducting resource allocation and benefit distribution in a fair, just, and transparent manner, eliminating unfair phenomena and barriers in the digital economy, safeguarding the rights and interests of participants in the digital economy, and promoting the sustainable development of the digital economy.
c) Ecological sustainability
The digital ecological system should possess the characteristics of an ecosystem, focusing on the interaction and mutual influence among entities in the digital economy, realizing circular utilization and sustainable development within the digital ecosystem, and avoiding negative impacts of digital economic activities on the environment.
d) Collaboration
The digital ecosystem should emphasize collaboration among digital economy entities to achieve coordinated development and shared prosperity of the digital economy, promoting mutual benefit and win-win cooperation among participants in the digital economy. This includes the goals and principles of co-building, co-sharing, co-existence, co-win, consensus, and co-governance, known as the "Six Co's."
e) Sustainability
The digital ecological system should pursue sustainable development to achieve long-term stability and healthy growth of the digital economy, focusing on the long-term interests and strategic planning among entities in the digital economy. It should enable self-optimization and evolution of the ecosystem to achieve the goal of creating sustainable value.
f) Innovation
The digital ecological system should encourage innovation and creativity among entities in the digital economy, promote technological innovation and business model innovation in the digital economy, enhance the core competitiveness and comprehensive strength of the digital economy, and drive the development and transformation of the digital economy.
2.The operational mechanism
The operational mechanism of the digital ecological system can be described in the following aspects:
a) Data sharing and openness
The operation of the digital ecological system requires extensive data sharing and openness. Data sharing can facilitate interaction and cooperation among participants, while also improving the quality and integrity of data. The openness of data can promote the emergence of new business models and products, thereby driving the development of the digital economy. Data within the digital ecological system should comply with requirements for privacy protection and data security to ensure the safety and legality of data.
b) Interconnection and technological innovation
The digital ecological system relies on various technologies and their innovation, such as artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, cloud computing, and others. These technologies can help participants in the digital ecological system collaborate and communicate more efficiently, promote the emergence of new business models and products, and enhance the security and reliability of the digital ecological system. At the same time, participants in the digital ecological system need to adhere to open standards and interoperability requirements to ensure interconnection among the various components of the digital ecological system.
c) Roles and Value Creation of Participants
The roles and value creation of participants in the digital ecosystem, including governments, businesses, individuals, and other organizations, are critical to the successful operation of the digital ecosystem. Governments need to formulate relevant policies and regulations to support and safeguard the digital ecosystem. Businesses and other organizations need to leverage their strengths in the digital ecosystem to provide better products and services and create more value. Individuals, as end users in most cases, can provide feedback on their needs, which can help the digital ecosystem better adapt to market demands. Of course, roles can be interchangeable during the actual operation.
d) Environmental Sustainability and Social Responsibility
The operation of the digital ecosystem needs to consider environmental sustainability and social responsibility to avoid irreversible damage to the environment and society. The digital ecosystem needs to adhere to principles such as low carbon, energy conservation, and circular economy to minimize its impact on the environment. Participants in the digital ecosystem also need to adhere to social responsibility and ethical standards, protect the privacy and rights of participants, and avoid misuse of data and technology.
e) Conclusion
In summary, the operational mechanism of the digital ecosystem is a complex and comprehensive issue that requires active participation from various stakeholders, including governments, businesses, individuals, and other roles, to collaborate. Governments should provide a favorable policy environment and legal protection to guide the development of the digital economy and ensure fair competition and data security in the process of digital transformation. Businesses should continuously promote technological innovation, improve digital operational efficiency, and actively assume social responsibility. Individuals need to constantly improve their digital literacy, fully utilize digital technology, and protect personal information and privacy. In addition, the development of the digital economy requires international cooperation and exchange to achieve global development and shared value of digital technology, while also paying attention to the impact of the digital economy on the ecological environment and promoting sustainable development of the digital ecosystem.
V. Approaches and Methods for Building a Digital Ecosystem
A. The Application of Digital Technologies in Building a Digital Ecosystem
Digital technologies play a crucial role in building a digital ecosystem. The goal and vision of a digital ecosystem is to create a digitalized ecosystem that facilitates efficient flow and sharing of information and data, and promotes rapid development of digital economy and digital society. Digital technologies, including but not limited to big data, artificial intelligence, blockchain, 5G, IoT and other emerging technologies, provide strong support for achieving the goals and vision of a digital ecosystem.
Firstly, big data technology enables rapid collection, storage, processing and analysis of massive amounts of data, providing data-driven insights and intelligent decision-making. Through big data technology, the digital ecosystem can better grasp market information, user needs, and social trends, achieving intelligent development of the digital economy.
Secondly, artificial intelligence technology can help the digital ecosystem achieve intelligent autonomous decision-making and optimization, improving the efficiency and quality of digital economic activities. For example, through intelligent customer service chatbots and intelligent advertising recommendation algorithms, the digital ecosystem can better meet user needs and increase digital economic revenue.
In addition, blockchain technology provides a distributed trust mechanism and data security guarantee for the digital ecosystem, effectively addressing trust issues in digital economic activities. At the same time, blockchain technology can also provide decentralized digital infrastructure for the digital ecosystem, enabling secure circulation and sharing of digital assets.
5G and IoT technologies provide faster, more reliable, and more secure communication and internet connectivity for the digital ecosystem, providing stronger technical support and infrastructure for the diversification and globalization of the digital economy. In the digital ecosystem, IoT can help achieve digitization and intelligence of various application scenarios, such as smart homes, smart cities, and smart manufacturing. IoT technology can connect various devices, facilities, sensors, etc., to collect and transmit various data in real time, thereby improving the operational efficiency and service quality of various application scenarios.
However, in the process of applying digital technologies in building a digital ecosystem, there are also a series of issues and challenges, such as data privacy protection, information security risks, technology innovation, and talent development. Therefore, the application of digital technologies in the digital ecosystem needs to take into account various factors and seek optimal solutions in light of the actual situation, in order to achieve sustainable development of the digital economy and inclusive sharing of the digital society.
B. The Ideas and Methods for Establishing a Digital Ecosystem
1.Objectives and Principles
The digital ecosystem needs to establish a digital economy infrastructure that can adapt to various industries, with a decentralized and distributed underlying architecture. Ensuring privacy for participants, data security, addressing the digital divide, algorithmic discrimination, and other related issues are of paramount importance. At the same time, the underlying architecture should support business operations. In addition, the establishment of a digital ecosystem needs to fundamentally address issues related to social credibility and fair transactions, avoiding speculation, market manipulation, unfair competition, monopolies, and uncontrolled expansion of capital. The digital ecosystem should also consider optimizing production relations, improving productivity, and changing production methods from an economic perspective. It should ensure the effective allocation of data elements and other production factors and resources throughout their lifecycle, realizing a combination of public and private ownership for all participants, and promoting the realization of labor-based distribution and common prosperity. The digital ecosystem should be built on a foundation of environmental sustainability. The digital ecosystem should have the ability to self-evolve. The establishment of the digital ecosystem aims to achieve the goals of "fairness, justice, transparency, mutual construction, sharing, coexistence, win-win, consensus, and governance", ultimately realizing a vision of world harmony and coexistence. These objectives and principles will guide the construction of the digital ecosystem and contribute to the sustainable operation and development of the digital economy.
2.Approach
The establishment of a digital ecosystem can be approached through the following aspects:
a) Define the objectives and values of the digital ecosystem
The construction of the digital ecosystem needs to define clear objectives and values, such as fairness, justice, transparency, mutual construction, sharing, coexistence, win-win, consensus, and governance. It should be inclusive and global in nature, aiming to achieve universal ownership, distribution based on labor and needs, and common prosperity for all participants. These objectives and values serve as the foundation of the digital ecosystem and the guiding principles throughout the construction process.
b) Build digital economy infrastructure
The construction of the digital ecosystem relies on the digital economy infrastructure, which utilizes emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and 5G. These technologies provide efficient and trustworthy governance mechanisms for the digital ecosystem, while also offering abundant data and information resources, enabling the digital ecosystem to become more intelligent, efficient, and secure.
c) Establish a decentralized and distributed underlying architecture
The construction of the digital ecosystem requires the establishment of a decentralized and distributed underlying architecture. This architecture can provide more flexible, efficient, reliable, and secure services, while avoiding the risks and monopolistic tendencies of centralization.
d) Adopt low-coupling design patterns such as toolboxes and plugins
The construction of the digital ecosystem should adopt low-coupling design patterns such as toolboxes and plugins. This can help increase the flexibility and scalability of the digital ecosystem, while also improving its maintainability and upgradability. In the construction of the digital ecosystem, different business scenarios and application requirements need to be addressed, hence low-coupling design patterns are necessary to easily add, replace, or remove corresponding components to adapt to different needs. Toolboxes, plugins, and other low-coupling design patterns can decouple different components, allowing them to work independently, while also providing more flexible configurations and management methods. In summary, adopting low-coupling design patterns such as toolboxes and plugins can provide a more flexible, scalable, and maintainable architecture for the construction of the digital ecosystem, better supporting the development of the digital economy and the realization of digital transformation, and facilitating the participation of various stakeholders in the co-construction of the digital ecosystem.
e) Ensure privacy and data security of participants
The construction of the digital ecosystem needs to ensure the privacy and data security of participants. In the era of the digital economy, the information and data of participants have become crucial production factors and resources. Protecting the privacy and data security of participants is an important aspect of the construction of the digital ecosystem. The digital ecosystem needs to establish effective privacy protection mechanisms and data security measures to ensure the information and data of participants are effectively protected.
f) Prioritize business perspectives in designing the underlying architecture
The construction of the digital ecosystem should prioritize business perspectives in designing the underlying architecture. The digital ecosystem needs to establish sound business models and revenue models, while also ensuring that it can provide more efficient, convenient, and secure services to various industries, thus providing stronger support for social and economic development.
g) Address issues of social trust and fair transactions
The construction of the digital ecosystem needs to address issues of social trust and fair transactions. The digital ecosystem needs to establish robust mechanisms for credit evaluation and fair transactions, to prevent malicious behavior and unfair competition, and to safeguard the healthy development of the digital ecosystem.
h) Ensure the circulation of data elements
The construction of the digital ecosystem needs to ensure the circulation of data elements. The circulation of data elements is an important aspect of the construction of the digital ecosystem, and it requires the establishment of open and shared mechanisms for data circulation, allowing data elements to flow freely within the digital ecosystem so that each role can access the required data resources to better fulfill their tasks. At the same time, a comprehensive set of data element standards and governance systems need to be established to ensure the quality and security of data elements.
i) Promote openness and innovation in the digital ecosystem
The construction of the digital ecosystem needs to promote openness and innovation, allowing more innovators to enter the digital ecosystem and drive its development. The digital ecosystem needs to establish open platforms and ecosystems, encouraging various innovative practices and experiments, while also establishing comprehensive intellectual property protection mechanisms to protect the interests of innovators. This will enable the digital ecosystem to self-evolve and sustainably develop.
j) Conclusion
The above are the ideas for building a digital ecosystem, which can help us better understand the process and importance of constructing a digital ecosystem. In the era of the digital economy, the digital ecosystem has become a crucial engine for driving economic development and social progress. Only by continuously improving the digital ecosystem can we better meet the needs of the people for a better life.
3.Methods
Establishing a digital ecosystem is a complex and long-term process that requires efforts in various aspects. Here are some methods:
a) Comprehensive promotion of digital transformation
Establishing a digital ecosystem involves extensive digital transformation by all stakeholders, including but not limited to governments, enterprises, and individuals. This provides policy support, infrastructure, and data assets for the digital ecosystem.
b) Strengthening data governance
Establishing a digital ecosystem requires robust data governance mechanisms. Governments, enterprises, and individuals need to actively participate in data governance, establishing effective mechanisms for data collection, processing, storage, and usage to ensure data quality and security.
c) Building public digital infrastructure
Establishing a digital ecosystem requires building public digital infrastructure, including data element circulation systems, digital identity authentication mechanisms, digital payment systems, etc. These infrastructure can provide public services and support for the digital ecosystem, promoting its construction and development.
d) Establishing a Digital Ecosystem Alliance
The construction of a digital ecosystem requires the establishment of a Digital Ecosystem Alliance, also known as an ecosystem consensus organization. Governments, enterprises, academic institutions, industry associations, experts, and others should participate jointly in the establishment of the Digital Ecosystem Alliance. Through collaborative research, development of standards and norms, and other means, the development and evolution of the digital ecosystem can be promoted.
e) Establishing regulatory and governance mechanisms for the digital ecosystem
The construction of a digital ecosystem requires the establishment of effective regulatory mechanisms, including aspects such as data security, privacy of stakeholders, integrity, and fair transactions. On one hand, the government, as a participant, should strengthen the regulation of the digital ecosystem to prevent misuse and monopoly. On the other hand, by utilizing emerging digital technologies such as "smart contracts," gradually transforming from a "human governance" to a unique "smart governance" system within the ecosystem, ensuring fairness, justice, and transparency. A sound governance system needs to be established. The digital ecosystem needs to rely on effective regulatory and management mechanisms, establish a sound legal and regulatory system, and strengthen the management and maintenance of the digital ecosystem, ensuring its normal operation and healthy development.
f) Establishing an economic model for the digital ecosystem
The construction of a digital ecosystem requires the establishment of a sound economic model to fundamentally optimize production relations, enhance productivity, and change production methods. This includes innovative business models, profit models, and distribution mechanisms, while also ensuring that the digital ecosystem can provide more efficient, convenient, and secure services to various industries, providing strong support for social and economic development.
g) Promoting international cooperation
The construction of a digital ecosystem requires promoting international cooperation, strengthening exchanges and cooperation with other countries and regions, and jointly promoting the construction and development of the digital ecosystem, promoting the prosperity and development of the digital economy.
h) Actively implementing policy support
The construction of a digital ecosystem requires policy support. The government needs to actively introduce corresponding policy measures, including financial support, tax incentives, talent introduction, innovation and entrepreneurship support, etc., to encourage and support the development of the digital economy and the construction of the digital ecosystem.
i) Strengthening talent cultivation and technology research and development
The construction of a digital ecosystem requires strengthening talent cultivation and technology research and development. Governments, enterprises, universities, and research institutions should strengthen talent cultivation, train a group of talents who master the core technologies of the digital economy, and strengthen technology research and development, continuously promoting the innovation and development of the digital economy and digital ecosystem.
j) Conclusion
In summary, the establishment of a digital ecosystem requires joint efforts from the government, enterprises, universities, research institutions, and other stakeholders. It requires establishing a collaborative model with multi-party participation and coordinated development, fully leveraging the strengths of all parties, promoting the construction of the digital ecosystem and the development of the digital economy, and providing strong support for social and economic development.
VI. Soft Infrastructure of Digital Ecosystem
A. Concept and Characteristics of Soft Infrastructure
1.Concept
Soft infrastructure, also known as software infrastructure, refers to a set of digital technologies, software, platforms, and services that support enterprise digitization and digital transformation, and help businesses and organizations undergo digital transformation. It is generally provided in the form of centralized SaaS platforms or software products and services. Compared to hardware infrastructure, soft infrastructure belongs to a different type of infrastructure that is more flexible and customizable, capable of quickly adapting to changing business needs and technological advancements.
2.Characteristics
Generality: Soft infrastructure is not only applicable to specific industries or organizations, but can also be widely used across different industries and organizations.
Customizability: The configuration and use of soft infrastructure can be customized according to the specific needs of the organization.
Agility: Soft infrastructure can quickly respond to business changes and technological advancements, making organizations more agile and innovative.
Networked: Soft infrastructure possesses networked and collaborative characteristics, supporting collaboration and data sharing among different geographic locations and departments.
Scalability: Soft infrastructure can be expanded and upgraded according to business growth needs to meet evolving business requirements.
Security: Soft infrastructure requires high levels of security to ensure the confidentiality and security of sensitive data and confidential information.
Data-driven: Soft infrastructure should provide insights based on data analysis and data mining to help organizations make more informed decisions and actions.
Cross-platform compatibility: Soft infrastructure typically has cross-platform compatibility, allowing it to run on different operating systems and hardware platforms, such as Windows, Linux, MacOS, etc.
Integrability: Soft infrastructure can be integrated with other software and systems, enabling it to work collaboratively with the organization's existing technological infrastructure.
Knowledge sharing: Soft infrastructure can facilitate knowledge sharing and learning, as best practices and experiences of digital transformation can be shared among different industries and organizations.
Resource sharing: The generality of soft infrastructure also means that resources and technology costs can be shared, as multiple organizations can share the costs and usage of soft infrastructure to achieve better cost-effectiveness.
Service standardization: The generality of soft infrastructure can result in standardized services, which helps improve service quality and reliability, reduce management and operational costs, and mitigate risks for businesses and organizations.
B. Soft Infrastructure in Digital Ecosystem
1.Overview
a) Concept
The soft infrastructure of the digital ecosystem is a collection of systems composed of distributed network applications. These distributed applications can operate independently or collaborate with each other, providing the foundational support for the digital ecosystem to function according to its intended goals. Its main function is to provide all participants in the digital economy with full-process participation in digital economic activities in accordance with the "three public" objectives and "six sharing" approach, ensuring comprehensive guarantees and support throughout the lifecycle of the digital economy.
Soft infrastructure is one of the core elements of the digital ecosystem. In the digital ecosystem, soft infrastructure serves as the cornerstone of the development of the digital economy, providing not only technical support but also strong guarantees for innovation in various application scenarios. Soft infrastructure has a significant promoting effect on production relations, productivity, and production modes, which can drive the continuous development and improvement of the digital economy. Compared with traditional soft infrastructure, the soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem has significant differences in deployment and network structure.
The soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem mainly includes digital identity networks, consensus-based governance networks, social (community, society) networks, financial transaction and payment networks, cross-platform API service networks, open-source co-building and contribution networks, data element circulation networks, big data and AI service networks, and human-computer interaction infrastructure.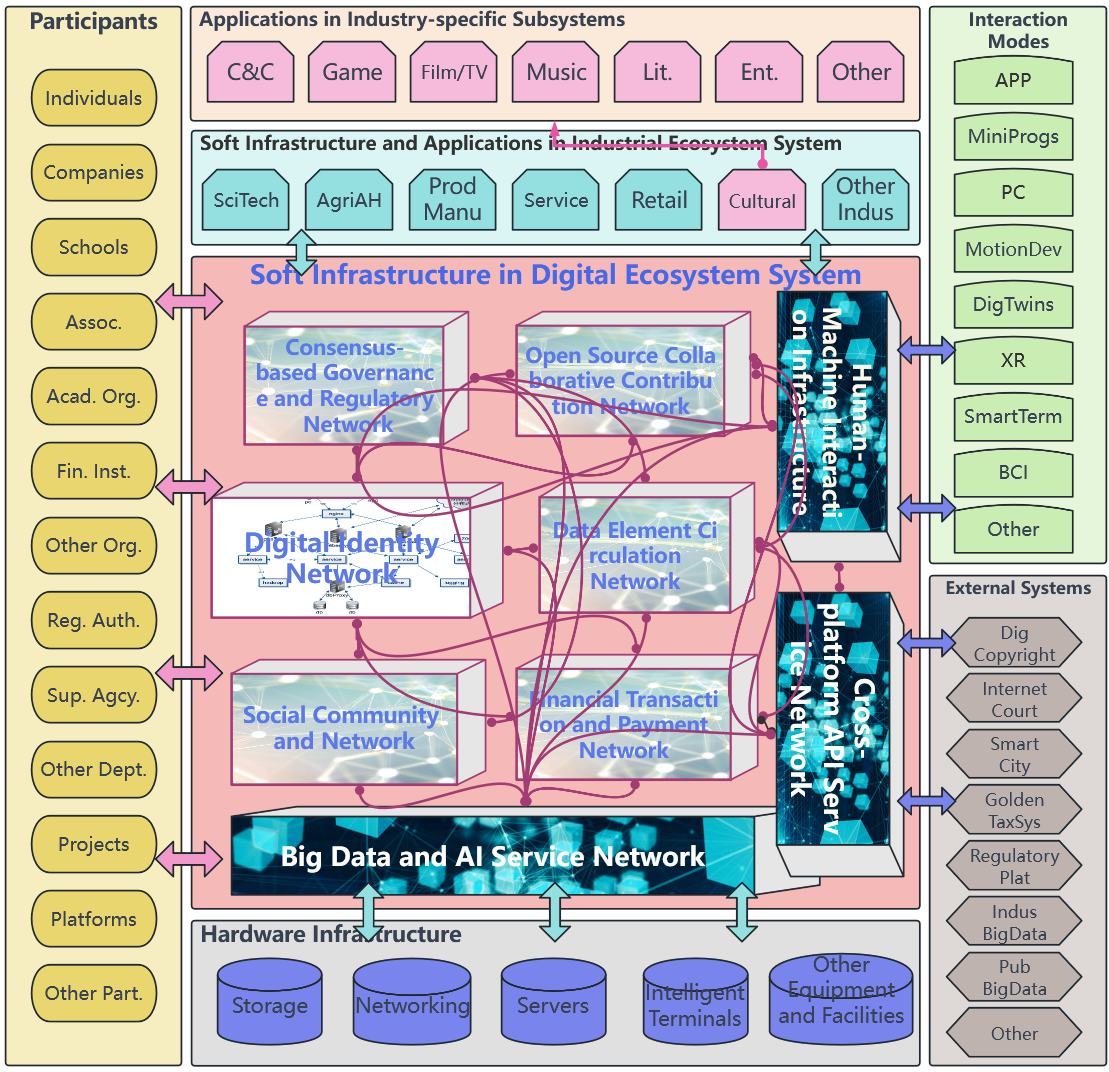
Architecture of Soft Infrastructure in Digital Ecosystem
b) Characteristics
1) Innovativeness
The design and implementation of the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem must adhere to the principle of innovativeness, promoting the development and application of digital technologies to meet the ever-changing market and user demands. The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to continuously explore new technologies and methods to achieve digital transformation and upgrading. In addition, the innovativeness of the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem also lies in the constant exploration and innovation of new business models. The development trend of the digital economy is constantly changing, with emerging business models continuously emerging, and the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem must be flexible and scalable to adapt to the changing market and user demands.
2) Openness and Scalability
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to be open and scalable. The digital ecosystem is formed by the collaboration and interdependence of various components, so the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to quickly adapt to different business requirements and technological changes. At the same time, the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem also needs to support open interfaces and standards for interaction and collaboration among various components.
3) Resilience and Reliability
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to be resilient and reliable. With the continuous expansion and development of the digital ecosystem, the software infrastructure needs to quickly adapt to environmental changes to ensure the stable operation of the digital ecosystem. At the same time, the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem also needs to have high reliability to ensure business continuity and reliability.
4) Security and Privacy Protection
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to have security and privacy protection. With the continuous expansion and development of the digital ecosystem, security and privacy issues have become increasingly important. The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to adopt multi-layered security measures and privacy protection mechanisms to protect the data and business security in the digital ecosystem.
5) Manageability and Monitorability
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to possess manageability and monitorability. The digital ecosystem is composed of numerous business components, thus the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem needs to be effectively managed and monitored to ensure the smooth operation and development of the digital ecosystem. Additionally, the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem also needs to support functionalities such as log recording and performance monitoring to enable timely detection and resolution of issues.
6) High Degree of Intelligence
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem typically integrates technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, enabling it to autonomously learn and adapt to user needs and environmental changes. For example, technologies such as intelligent customer service and machine translation are widely applied in the digital ecosystem, making it more intelligent and efficient.
7) Networked and Distributed
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem usually adopts a distributed network structure, allowing data and information to flow and exchange among different devices, systems, and platforms. For example, applications such as digital currencies and smart contracts based on blockchain technology enable decentralized transactions and value circulation.
8) Open Source, Collaborative Development and Sharing
Open source, collaborative development, and sharing are also important characteristics of the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem. In the digital ecosystem, the software infrastructure is often developed and maintained through collaborative efforts of multiple organizations, enterprises, individuals, etc. Open source refers to the practice of making software code open for others to view, use, modify, and share. By embracing open source, more developers can participate in software development, improving the quality and stability of the software. At the same time, open source can promote knowledge sharing and technological innovation, contributing to the growth and expansion of the digital ecosystem. Collaborative development involves cooperation and joint efforts among different parties in the software development process to collectively promote the development and maintenance of the software. Through collaborative development, resources from different parties can be integrated to improve the efficiency and quality of software development. Sharing refers to sharing the outcomes of software development with others, so that more people can benefit from the convenience brought by the software. Sharing promotes collaborative development in the digital ecosystem and enhances the overall competitiveness of the digital ecosystem.
c) Differences from Traditional Software Infrastructure
1) Higher degree of networking
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem relies more on distributed networks, with a higher degree of networking. In contrast, traditional digital software infrastructure relies more on centralized network hardware devices such as standalone computers, servers, and cloud computing.
2) More openness, sharing, and interoperability
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem is more open, shared, and interoperable, allowing for interoperability among different systems and information sharing. In contrast, traditional digital software infrastructure is often provided by a few large vendors, with higher levels of closed source, and poor interoperability among different systems.
3) Data-driven
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem places a higher emphasis on data collection, analysis, and utilization, enabling more intelligent services. In contrast, traditional digital software infrastructure typically focuses more on functional implementation of systems.
4) Focus on ecosystem construction and maintenance
The software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem places more emphasis on ecosystem construction and maintenance, including platform security, sustainability, and other aspects. Traditional digital software infrastructure tends to focus more on system availability and stability.
2.Digital Identity Network
a) Concept
A digital identity network is a networked system for identifying and verifying the identity of individuals or entities, built on digital technology and distributed networks. It uses digital identity credentials, authentication, authorization, and management mechanisms to establish unique identification and trusted authentication of participants in the digital world, enabling controlled and manageable identities in the digital society. Individual identities are relatively independent and can be authorized to join different roles in organizations, companies, and government departments, allowing for participation in the ecosystem with different roles and varying social and economic activities.
b) Functions
The main functions of a digital identity network include, but are not limited to:
1) Unified identity verification
A digital identity network can employ various methods for identity verification, such as passwords, biometric features, digital certificates, etc., to ensure the authenticity and legitimacy of individual or entity identities. This helps prevent identity fraud and impersonation, protecting the legitimate rights and interests of individuals, organizations, companies, and governments. It can provide convenient identity verification methods for various online services, eliminating the need for users to repeatedly input identity information, simplifying the identity verification process, and improving user experience. At the same time, a digital identity network can support cross-platform and cross-system identity verification and management, providing a unified identity management experience.
2) Identity role management
A digital identity network can centralize the management and authorization of individual identity information through digital identity credentials and identity management systems. Participants can autonomously manage and control their own identity information, including identity authentication, authorization, and sharing of identity data, as well as the management of data elements for proof of ownership and digital currency. It supports the granting and maintenance of roles such as digital citizens, digital employees, digital regulators, etc., in the digital ecosystem, enabling autonomous management and utilization of identities.
3) Privacy Protection and Data Security
Digital identity networks need to have robust mechanisms for data security and privacy protection to ensure that digital identity information is not misused, leaked, or tampered with. In a digital identity network, participants have control over their own identity and data by default, and when accessing applications or third-party applications in the digital identity ecosystem, it is assumed to be pseudonymous login. If an application needs to access personal privacy data from a digital identity, it requires authorization from the participant. Data generated from social and economic activities within the digital identity ecosystem are owned by the digital identity, and if joint ownership is required, it needs to be authorized based on consensus. In summary, digital identity networks enable participants to autonomously manage and control their own identity information, protecting the privacy rights and information security of all participants.
4) Support for Digital Economy Development
Digital identity networks provide a foundational infrastructure for the development of the digital economy, promoting interconnectivity and collaborative sharing of digital economy elements such as finance, e-commerce, and social networks. Through digital identity networks, users can achieve identity verification and identity management across different platforms and systems, facilitating the interconnection and cooperation of the digital economy. Digital identity can effectively ensure the full lifecycle management of data elements.
5) Innovation in Social Services
Digital identity networks have broad application potential in fields such as government services, healthcare, and social security. Through digital identity networks, governments can provide more convenient and efficient government services, healthcare institutions can achieve precise identity authentication and healthcare information management, and social security systems can achieve intelligent identity verification and welfare distribution.
6) Fairness and Inclusivity
Digital identity networks can provide new identity verification methods for those who lack traditional means of identity authentication or face difficulties in identity verification. For example, digital identity networks can provide more inclusive and fair identity verification methods for people without identification or bank accounts, immigrants or refugees, and the impoverished population, enabling them to integrate into the digital society and enjoy corresponding rights and services.
7) Inclusive Finance and Financial Inclusion
The digital identity network can provide secure and efficient means of identity authentication and digital credit rating system for ecological finance, promoting inclusive finance and financial inclusion. Through the digital identity network, users can conveniently engage in online payment, loans, investments, and other financial activities, promoting the accessibility of financial services and improving financial inclusion.
8) Reducing the Occurrence of Crime and Terrorism
The digital identity network can assist ecological systems and regulatory agencies in achieving stricter regulation. Through digital identity identification and authentication methods, users can be verified and assessed for risk, and their activities in all ecological domains can be recorded through distributed ledger technology that integrates with internet courts and regulatory and judicial departments. This information can be provided to law enforcement and regulatory agencies within the legal and consensus framework, helping to prevent crime and terrorism.
9) Social Networks and Digital Social Interaction
The digital identity network can provide secure and trusted means of identity authentication and authorization for social networks and digital social interactions, protecting user information and privacy, preventing fake accounts and information leakage, and enhancing the security and trustworthiness of social networks and digital social interactions. This can optimize social relationships, production relationships, and social integrity.
10) Digital Government and E-Governance
The digital identity network can support the development of digital government and e-governance, achieving digitization, intelligence, and convenience of government services. Through the digital identity network, the government can realize online identity authentication, digital signatures, digital certificates, and other functionalities, providing efficient, secure, and convenient government services, promoting interconnectivity and cooperative sharing between the government and citizens.
3.Consensus-based and Co-governance Regulatory Network
a) Concept
The "Consensus-based and Co-governance Regulatory Network" is one of the important soft infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, providing digital means and tools for all participants to achieve consensus in a fair, just, and transparent manner. It can support consensus building at various levels, from the development of the entire ecosystem to the regulation and standards of industries, and effectively govern and regulate social and economic activities in the entire ecosystem through digital methods such as smart contracts. The goal of this network is to facilitate consensus among all parties in a fair environment, ensure the self-optimization of the ecosystem, and enforce compliance through non-human means, thereby reducing social trust costs, accelerating social and economic development, and changing the relationship among participants to focus more on service and product quality without worrying about unfairness.
b) Functions
The functions of the "Consensus-based and Co-governance Regulatory Network" include but are not limited to:
1) Providing reliable consensus mechanisms and tools
The Consensus-based and Co-governance Regulatory Network provides a fair, just, and transparent platform for all participants, enabling them to achieve consensus in a relatively fair environment. Through digital means and tools, such as blockchain, smart contracts, etc., consensus can be reached and recorded, ensuring that the interests of all parties are treated equally.
2) Supporting the development and regulation of the ecosystem
The Consensus-based and Co-governance Regulatory Network can not only support the sustainable development of the entire digital ecosystem but also help establish industry norms and standards. Through consensus mechanisms and digital methods such as smart contracts, parties can reach consensus in the network, jointly formulate and comply with norms and standards, thereby promoting the regulation and healthy development of the entire ecosystem.
3) Governance and regulation of the ecosystem
The consensus-based governance and regulation network enables effective governance and regulation of social and economic activities within the digital ecosystem through digital means such as smart contracts. Through the execution and recording of contracts, compliance with consensus and traceability of violations can be achieved, reducing the cost of social trust and mitigating potential risks and violations.
4) Facilitating cooperation and win-win outcomes among stakeholders
The consensus-based governance and regulation network emphasizes equality and cooperation among stakeholders, enabling them to reach consensus in a fair environment through consensus mechanisms and digital means. This promotes cooperation and win-win outcomes among stakeholders, fostering stability and sustainable development of the digital ecosystem.
5) Promoting social and economic development
The consensus-based governance and regulation network can automate consensus operations and executions, reducing human intervention and interference through digital means. This improves efficiency, lowers costs, and promotes social and economic development. Stakeholders can focus on service and product quality without worrying about unfair practices, thereby fostering a healthy development of the digital ecosystem.
6) Reducing information asymmetry and integrity risks
The consensus-based governance and regulation network helps reduce information asymmetry and integrity risks. Through digital means and tools, stakeholders can publicly record and share information in the network, increasing transparency and traceability of information. This helps reduce information asymmetry, enhance trustworthiness among stakeholders, and lower integrity risks.
7) Improving Social Governance and Regulatory Efficiency
Consensus-based and co-governed regulatory networks can provide a more efficient and intelligent way for social governance and regulation. Through digital means and technologies such as smart contracts, real-time monitoring and traceability of social and economic activities can be achieved, thereby improving the efficiency of regulation and reducing resource wastage. Consensus mechanisms and digitized approaches can also encourage parties to comply with rules and agreements, thereby improving the effectiveness of social governance.
8) Promoting Innovation and Development
Consensus-based and co-governed regulatory networks can promote innovation and development. Through consensus mechanisms and digital approaches, parties can freely express opinions, share experiences, and collaborate on innovation in a fair environment. This helps to stimulate the innovation potential of all parties, promote technological and business innovation in the digital ecosystem, and thereby promote sustainable economic development.
9) Strengthening Social Consensus and Cohesion
Consensus-based and co-governed regulatory networks can strengthen social consensus and cohesion. Through consensus mechanisms and digital approaches, parties can reach consensus in the network and form mutually recognized norms and standards. This helps to enhance cooperation and trust among parties, and promotes harmonious and stable social development.
10) Conclusion
In summary, as an important soft infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, consensus-based and co-governed regulatory networks can promote consensus among parties in a fair, just, and transparent environment, support the development and regulation of the ecosystem, achieve governance and regulation of the ecosystem, promote cooperation and win-win among participants, reduce information asymmetry and integrity risks, improve social governance and regulatory efficiency, promote innovation and development, strengthen social consensus and cohesion, and thereby drive the healthy and sustainable development of the digital ecosystem.
4.Social (Community) Networks
a) Concept
Distributed social networks are one of the important infrastructures in the digital ecosystem, serving as means and tools to support communication, interaction, and activity organization among participants. They utilize distributed computing and blockchain technology to store user data in a decentralized manner across multiple nodes, emphasizing user ownership and privacy protection of data, allowing users to have autonomous control over data usage and sharing. Distributed social networks promote the formation of communities and allow users to establish connections through direct communication and collaboration among nodes, without relying on centralized platforms. Integration of blockchain technology can enhance the transparency and security of social networks, reducing the risks of information asymmetry and data tampering, and motivating user participation and contribution through incentive mechanisms, driving the continuous development and innovation of social networks. Distributed social networks aim to protect user rights, achieve community self-governance, and integrate with digital identity networks and consensus-based governance networks for automated regulation of illegal activities, effectively preventing violations of consensus and promoting the healthy and sustainable development of the digital ecosystem.
b) Functions
Social (community) networks play important roles in the digital ecosystem, including but not limited to the following aspects:
1) Communication and interaction
Social (community) networks provide a convenient and real-time platform for communication and interaction among all participants, serving as the networking system to ensure the normal conduct of social and economic activities and support production relations. Participants can establish connections, share information, communicate, and collaborate with other participants through distributed social networks, facilitating information dissemination and knowledge sharing, and enriching users' social experiences.
2) Organization of activities
Social (community) networks provide convenience for participants to organize activities. Users can create and manage communities, groups, or events through social networks, inviting other participants to join and participate in activities of common interest, thus promoting the formation and development of communities and groups. Physical participants can also use social networks to build their own private traffic, conduct marketing, promotion, and feedback activities.
3) Ownership and privacy protection of participant data
Distributed social networks emphasize the ownership and privacy protection of participant data. Participant data is stored in a decentralized manner on multiple nodes, and participants can autonomously control the use and sharing of data, reducing the risk of personal and entity information being abused or leaked, and enhancing participants' control over their own information.
4) Community self-governance
Distributed social networks encourage community self-governance, allowing participants to participate more autonomously in decision-making and management within the social network. Through direct communication and collaboration between nodes, participants can jointly participate in the management and operation of communities, forming a more open, fair, and democratic social network ecosystem, which is a part of the digital ecosystem along with the industry ecosystem.
5) Transparency and security
The integration of blockchain technology can enhance the transparency and security of social networks. Blockchain technology can record interaction information and user behavior in social networks, ensuring the authenticity and traceability of data, reducing the risks of information asymmetry and data tampering. At the same time, blockchain technology can provide higher security, protecting user data from malicious attacks and infringement.
6) Incentive Mechanisms
Distributed social networks often adopt incentive mechanisms to encourage user participation and contributions. For example, users can be rewarded for valuable improvement suggestions, technical expertise, storage, computing power, content creation, participation in community activities, and promotion of the ecosystem, among others, to promote active participation of stakeholders in the digital ecosystem and drive continuous development and innovation of the digital ecosystem.
7) Automated Regulation
Distributed social networks integrate digital identity networks and consensus-based governance networks, enabling automated regulation of illegal activities. Through smart contracts and consensus algorithms, monitoring and penalties for illegal activities in social networks can be automated, ensuring the security and legality of social networks. This helps reduce the spread of false information, fraud, infringement, and other illegal activities in social networks, safeguarding user rights and the healthy development of social networks.
8) Formation and Development of Communities
Distributed social networks can promote the formation and development of communities. Participants can freely create and manage communities, groups, or events in social networks, invite other participants to join, forming communities and groups with common interests or goals. This helps participants find like-minded individuals, establish connections, share information and resources, and build close social relationships, promoting the prosperity and innovation of communities.
9) Benign and Sustainable Development of the Digital Ecosystem
As one of the infrastructures of the digital ecosystem, distributed social networks emphasize data ownership and privacy protection of participants, community autonomy, transparency, and security through features such as incentive mechanisms. This helps promote the benign and sustainable development of the digital ecosystem by reducing the monopoly of centralized platforms over user data and behavior, increasing user control over data and social networks, promoting user participation and contributions, and driving diversification, innovation, and sustainability of the digital ecosystem.
5.Financial Transaction and Payment Network
a) Concept
A financial transaction and payment network is a financial system built on decentralized and distributed network using distributed ledger technology (DLT) to facilitate peer-to-peer financial transactions and payments, with the aim of reducing transaction costs, improving efficiency, increasing transparency, and enhancing security. Its core objective is decentralization, promoting financial inclusion and innovation, and driving the financial industry towards a more open, efficient, and inclusive direction. The financial transaction and payment network supports payment functionalities and decentralized financial functionalities, providing diversified and flexible digital financial services through innovative applications such as smart contracts, lending platforms, digital asset trading platforms, etc. Overall, the financial transaction and payment network will play an important role in the future digital financial industry and digital economy ecosystem, bringing new challenges and opportunities to the traditional financial system and regulatory frameworks.
b) Functions
As one of the foundational infrastructures of the digital ecosystem, the financial transaction and payment network plays a crucial role in the digital economy, primarily in the following aspects:
1) Facilitating peer-to-peer financial transactions and payments
The financial transaction and payment network enables peer-to-peer financial transactions and payments through decentralized and distributed networks, without relying on traditional financial intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and improving transaction efficiency.
2) Providing convenient and efficient payment tools
The financial transaction and payment network offers convenient and efficient payment tools for various types of transactions in the digital economy, including digital currencies, digital payment methods, etc., facilitating transactions and payments between users. For example, in China, easy access to digital RMB as a primary form of currency and gradually promoting the internationalization of digital RMB, while also accommodating various countries' government-issued digital currencies.
3) Increased transparency and security of transactions
The financial transaction payment network adopts distributed ledger technology, where transaction records are publicly recorded on the blockchain, increasing transaction transparency, and uses encryption algorithms to protect transaction security, reducing potential financial risks.
4) Promoting financial inclusion
The decentralized nature of the financial transaction payment network provides equal opportunities for financial services to small and micro enterprises, individual operators, and unbanked populations that are not covered by traditional financial systems, promoting financial inclusion. It can help reach populations that are difficult for traditional financial systems to access, including rural areas, low-income groups, and more, providing them with financial services and support, promoting inclusive finance.
5) Encouraging financial innovation
The financial transaction payment network supports innovative applications such as smart contracts, providing a technological foundation for financial innovation, and promoting the development and application of digital assets and digital financial products, driving financial innovation in the digital economy.
6) Providing diversified and flexible digital financial services
Through innovative applications such as decentralized lending platforms, digital commodity trading platforms, and data element trading platforms, the financial transaction payment network provides diversified and flexible digital financial services to meet the financial needs of different participants in the digital economy. It supports diversified financial assets and transactions, including digital currencies, digital securities, data assets, data elements, etc., promoting market diversification and asset diversification, providing investors and participants with more choices and opportunities.
7) Promoting sustainable development of the digital economy
By reducing transaction costs, improving transaction efficiency, and promoting financial inclusion, the financial transaction payment network contributes to the sustainable development of the digital economy, promoting inclusive economic and social growth.
8) Supporting the application of digital assets
The financial transaction and payment network provides support for the issuance, trading, and management of digital assets, promoting the application and promotion of digital assets in the digital economy, and expanding the financial ecosystem of the digital economy. By integrating with infrastructure such as digital identity networks and data element circulation networks, it can provide support for the full lifecycle management of goods, services, data information, and digital assets.
9) Enhancing the security of the financial system
The financial transaction and payment network adopts distributed ledger technology and encryption algorithms to enhance the security of the financial system, reducing potential financial risks and fraudulent activities, and enhancing the stability and reliability of the financial system.
10) Promoting financial compliance and regulatory innovation
The application of the financial transaction and payment network in the digital economy has brought new challenges and opportunities to the traditional financial system and regulatory framework. It promotes financial compliance and regulatory innovation, prompting regulatory agencies and policymakers to focus on the regulation and innovation of financial activities in the digital economy, aiming for mutual participation and compliance among regulatory agencies and industry participants.
11) Promoting the development of the digital economy ecosystem
As one of the soft infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, the financial transaction and payment network promotes the development of the digital economy ecosystem. It provides convenient and efficient solutions for various transactions and payments in the digital economy, as well as decentralized inclusive finance, which will undoubtedly promote the flourishing development of the digital economy.
12) Enhancing Financial Service Experience
The financial transaction and payment networks provide diverse and flexible digital financial services, enriching the forms and methods of financial services and enhancing the experience of participants. This meets the needs of various participants in the digital economy for convenient, efficient, and secure financial services.
13) Promoting Internationalization of the Digital Economy
The cross-border payment functionality and decentralized nature of financial transaction and payment networks help promote the internationalization of the digital economy. It enables cross-border payments, eliminates geographical and national boundaries in the traditional financial system, and facilitates global cross-border exchanges and collaborations in the digital economy. It can promote cooperation and exchanges in the digital economy among different countries and regions, and drive the international development of the digital economy.
14) Improving Financial Efficiency and Reducing Transaction Costs
Financial transaction and payment networks can achieve real-time clearing and settlement, reducing cumbersome procedures and intermediaries in the traditional financial system, improving financial efficiency, and lowering transaction costs. This has a positive impact on the operation and transaction efficiency of financial markets.
15) Conclusion
The above-listed are some of the important roles and impacts of financial transaction and payment networks in the digital economy. With the continuous development of the digital economy and innovation in financial technology, financial transaction and payment networks will continue to play a significant role in the digital economy and have a profound impact on the financial system and economic activities.
6.Cross-Platform API Service Network
a) Concept
The cross-platform API service network is a software infrastructure built on digital technology, designed to connect application programming interface (API) services of different digital systems within and outside the digital ecosystem, enabling data and function exchange across systems, platforms, and ecosystems. By providing standardized API interfaces and protocols, the cross-platform API service network enables applications from different systems to call and interact with each other, facilitating data transfer, function invocation, and business process integration. The core objective of the cross-platform API service network is to promote interconnectivity among digital ecosystems, providing unified API interfaces and standardized data exchange methods, thus reducing the technical integration costs between different ecosystems, accelerating application development and deployment, and facilitating collaborative development of the digital economy ecosystem.
b) Functions
As a software infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, the cross-platform API service network performs the following important functions in the digital economy:
1) Facilitating interconnectivity among digital ecosystems
The cross-platform API service network enables applications from different digital ecosystems within and outside to call and interact with each other by providing standardized API interfaces and protocols. This facilitates interconnectivity among digital ecosystems, facilitating seamless exchange of data and functions, and strengthening cooperation and collaboration between ecosystems.
2) Reducing technical integration costs
Technical integration between different digital systems often faces challenges such as different programming languages, data formats, and protocols, resulting in high integration costs. The cross-platform API service network reduces the technical integration costs between different systems by providing standardized API interfaces and protocols, accelerating application development and deployment.
3) Accelerating application development and deployment
The cross-platform API service network provides unified API interfaces and standardized data exchange methods, allowing applications to be developed and deployed quickly on different platforms. Developers can integrate functionality and business processes by calling APIs from the cross-platform API service network, thereby speeding up the development and deployment process of applications and improving development efficiency.
4) Enhancing flexibility and innovation of the digital economy ecosystem
The openness and extensibility of the cross-platform API service network allow third-party applications to access and extend its functionalities, promoting innovation and diversity within the digital ecosystem. Different digital systems can communicate and share data and functions through the cross-platform API service network, thereby enhancing the flexibility and innovation of the digital economy ecosystem. For example, by accessing platforms such as internet courts, digital copyright authentication centers, tax systems, and other regulatory systems.
5) Supporting cross-platform collaboration in the digital economy ecosystem
The cross-platform API service network enables applications from different digital ecosystems within and outside to integrate functionality and business processes by calling each other's APIs, thereby promoting cross-platform collaboration within the digital economy ecosystem. Enterprises, developers, and users within different ecosystems can share data and collaborate on innovation through the cross-platform API service network, thereby driving collaborative development of the digital economy ecosystem.
6) Provide security and authentication mechanisms to protect user privacy and data security
Cross-platform API service networks typically have security and authentication mechanisms in place to ensure secure transmission and invocation of data and functions, protecting the privacy and data security of all parties involved. This helps establish trust within and outside the digital ecosystem, promoting cooperation and communication among different digital economy ecosystems.
7) Foster innovation and application of digital technologies
As the underlying infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, cross-platform API service networks not only connect API services from different digital systems, but also provide developers with convenient interfaces and standardized data exchange methods, thereby promoting innovation and application of digital technologies. Through cross-platform API service networks, developers can quickly invoke functions and data from other systems, driving continuous innovation and evolution of applications within the digital economy ecosystem.
8) Facilitate expansion and extension of the digital ecosystem
The openness and scalability of cross-platform API service networks support the expansion and extension of the digital ecosystem. Enterprises, developers, and users from different ecosystems can connect and interact through cross-platform API service networks, enabling resource sharing and collaborative innovation, thus promoting the expansion and extension of the digital ecosystem, forming a more complete and enriched digital economy ecosystem.
9) Conclusion
In summary, as the underlying infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, cross-platform API service networks play an important role in the digital economy, facilitating interconnectivity within and outside the digital ecosystem, reducing technology integration costs, accelerating application development and deployment, improving flexibility and innovation, supporting cross-platform collaboration, protecting user privacy and data security, promoting innovation and application of digital technologies, and facilitating expansion and extension of the digital ecosystem. These roles contribute to the collaborative development of the digital economy ecosystem and promote innovation and growth in the digital economy.
7.Open Source Collaborative Contribution Network
a) Concept
The open source collaborative contribution network is an open collaboration model based on community autonomy and democratic participation, aimed at promoting cooperation and collaboration within the digital ecosystem system. It connects stakeholders such as expert groups, think tanks, developers, and technology companies from around the world, forming an open, transparent, and inclusive community ecosystem. It provides a fair, just, and transparent way for all stakeholders to participate in the technological support of the ecosystem. The open source collaborative contribution network designs an open model that allows all stakeholders to participate, provide optimization suggestions, technical support, storage and computing power, education and promotion, as well as quantification and reward records for these contributions. It is also a distributed and decentralized open sharing system. As one of the software infrastructures of the digital economy ecosystem, the open source collaborative contribution network plays important functions in promoting technological innovation and development, reducing software development costs, improving software quality and security, and promoting global cooperation and knowledge sharing in the digital economy.
b) Functions
The open source collaborative contribution network, as one of the software infrastructures of the digital ecosystem, plays important functions in the digital economy, including but not limited to:
1) Promoting technological innovation and development
The open source collaborative contribution network connects developers, technology companies, and other stakeholders from around the world, providing an open, transparent, and inclusive community ecosystem. In this ecosystem, stakeholders can collaborate, cooperate, share, and communicate, thus promoting technological innovation and development. By collectively participating in the construction and contribution of open source projects, stakeholders can jointly drive the continuous advancement of technology, enabling sustainable development of the digital economy.
2) Lowering the Cost of Ecosystem Development
The open-source collaborative contribution network allows all parties to participate in open-source projects, providing optimization suggestions, technical support, storage, and computing resources. This can lower the cost of software development, avoid redundant development work, and improve development efficiency. Through sharing open-source resources and collaboration within the community, all parties can more efficiently develop and utilize ecosystems in the digital economy, thereby reducing the development costs in the digital economy and achieving the goal of co-building, sharing, and win-win.
3) Enhancing Ecosystem Quality and Security
The open-source collaborative contribution network adopts an open and transparent collaborative mode based on ecosystem consensus, and all participants can contribute to and review open-source projects. This helps improve the quality and security of ecosystems. Through the participation of numerous developers and technology companies, multi-faceted review and improvement of the ecosystem can be conducted, reducing potential security vulnerabilities and defects, and enhancing the quality and security of the ecosystem, contributing to information security and data privacy protection in the digital economy.
4) Promoting Global Cooperation and Knowledge Sharing
The open-source collaborative contribution network connects participants from around the world, forming an open, transparent, and inclusive community ecosystem. In this ecosystem, all parties can participate, collaborate, and exchange ideas, promoting global cooperation and knowledge sharing. Through the open-source collaborative contribution network, knowledge, experience, and technology of open-source projects can be shared, promoting technology cooperation and innovation on a global scale, contributing to globalization and cross-border cooperation in the digital economy.
5) Conclusion
In summary, as one of the software infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, the open-source collaborative contribution network plays an important role in the digital economy, including promoting technological innovation and development, lowering the cost of ecosystem development, enhancing ecosystem quality and security, and promoting global cooperation and knowledge sharing. Through an open, transparent, and inclusive community ecosystem, the open-source collaborative contribution network provides all participants with a fair, just, and open way to participate in ecosystem technology support, encouraging collaborative work, cooperation, sharing, and communication among all parties, thereby driving innovation, development, and globalization cooperation in the digital economy.
8.Data Element Circulation Network
a) Concept
The data element circulation network is a distributed software infrastructure based on digital technology, aiming to facilitate the circulation and sharing of data elements among different stakeholders. This network covers various participants, such as enterprises, government agencies, academia, social organizations, and individuals, and utilizes digital technology for data element generation, rights confirmation, collection, transmission, transaction, processing, reprocessing, utilization, profit distribution, and sharing, etc. Its purpose is to achieve efficient utilization and value creation of data elements, providing an open, transparent, secure, and trustworthy environment for different stakeholders to safely share data elements and collaborate on data analysis, mining, and applications.
The importance of the data element circulation network lies in promoting the circulation and sharing of data elements, and driving the development and innovation of the digital economy. It should be noted that the establishment of the data element circulation network should be done in a lawful and compliant manner, protecting data privacy and security, and complying with laws, regulations, and ethical principles as ecological consensus, to ensure the legitimate, secure, and reliable use of data. At the same time, the data element circulation network should also focus on the quality, authenticity, and credibility of data, ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of data circulation and sharing. Only under the premise of legality and compliance, can the data element circulation network fully play its role in promoting the development of the digital economy.
The data element circulation network is the core software infrastructure of the digital economy, supporting the management lifecycle of data elements as a complete closed loop.
b) Functions
As one of the soft infrastructure of the digital ecosystem, the data element circulation network plays a crucial role in the digital economy. The following are several important functions of the data element circulation network in the digital economy:
1) Facilitating the circulation and sharing of data elements
The data element circulation network connects various stakeholders in the digital ecosystem, including enterprises, government agencies, academia, social organizations, and individuals, through digital technology, enabling efficient circulation and sharing of data elements. This helps eliminate data silos, promote cooperation and collaboration among parties, and facilitate cross-border circulation of data elements, thereby enhancing the efficiency of data utilization and the creativity of data value.
2) Supporting the generation and development of the digital economy
The data element circulation network is the core software infrastructure of the digital economy, providing fundamental support for the generation and development of the digital economy. Through the data element circulation network, enterprises and individuals can more conveniently access and use data elements, thereby driving innovation and development in various fields of the digital economy, including artificial intelligence, big data analytics, Internet of Things, and other domains.
3) Providing an open, transparent, secure, and trustworthy environment
The data element circulation network needs to be established on a legal and compliant basis, protecting data privacy and security, and adhering to laws, regulations, and ethical principles as the ecological consensus. By establishing an open, transparent, secure, and trustworthy environment, the data element circulation network can enhance trust among stakeholders in data circulation and sharing, thereby promoting the healthy development of the digital economy.
4) Facilitating data analysis, mining, and application
The data element circulation network provides a platform for stakeholders to exchange, transfer, process, and share data elements, supporting data analysis, mining, and application. Different stakeholders can share data elements, collaborate on data analysis, mining, and application by integrating with digital identity networks, big data AI service networks, and other soft infrastructure, thereby promoting data-driven decision-making and innovation in the digital economy.
5) Focusing on data quality and credibility
The data element circulation network needs to focus on the quality, authenticity, and credibility of data, ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of data circulation and sharing through evaluation processes. High-quality, authentic, and trustworthy data elements can improve the accuracy and effectiveness of data applications, thereby promoting the development of the digital economy.
6) Conclusion
In summary, as one of the soft infrastructures of the digital ecosystem, the data element circulation network plays a significant role in promoting the circulation and sharing of data elements, supporting the generation and development of the digital economy, providing an open, transparent, secure, and trustworthy environment, and facilitating data analysis, mining, and application.
9.Big Data AI Service Network
a) Concept
The Big Data AI Service Network is a high-availability service cluster consisting of distributed servers, designed to store and process large-scale data and provide rich artificial intelligence toolkits, aiming to provide intelligent support for social and economic activities in the digital ecosystem. This network supports big data storage, processing, and AI services, providing secure and reliable data processing and intelligent support for the digital ecosystem. It features high distribution and scalability, capable of handling the demands of large-scale data processing and computation, with flexible resource expansion based on business needs. In addition, the Big Data AI Service Network promotes the data-driven transformation and value creation in the digital economy, facilitating rapid development and innovation of various industries on emerging foundations, driving the prosperity and innovation of the digital economy.
b) Functions
As a foundational infrastructure in the digital ecosystem, the Big Data AI Service Network plays critical functions in the digital economy.
1) Provides storage and computing power
The Big Data AI Service Network provides efficient big data storage and computing capabilities for the digital economy. With the rapid development of the digital economy, a large amount of data is generated, including structured and unstructured data such as user behavior data, social media data, sensor data, etc. These data contain rich information and value, but traditional data processing and analysis methods struggle to cope with the challenges of large-scale data. The Big Data AI Service Network, through the high-availability service cluster of distributed servers, can efficiently store and process large-scale data, providing powerful data processing capabilities for the digital economy.
2) Provides rich artificial intelligence toolkits
The Big Data AI Service Network provides diverse artificial intelligence toolkits to support intelligent data processing and analysis. Artificial intelligence technologies play a critical role in the digital economy, enabling extraction of valuable information from massive data through techniques such as data mining, machine learning, and deep learning, and providing scientific basis for business decision-making. The Big Data AI Service Network offers a variety of artificial intelligence toolkits, allowing users to quickly build and deploy various types of AI models, thus achieving intelligent processing and analysis of data and providing powerful technical support for the development of the digital economy.
3) Meets the demand for ecological big data processing and computation
The Big Data AI Service Network features high distribution and scalability, capable of addressing the demand for large-scale data processing and computation in the digital economy. The volume of data in the digital economy is experiencing explosive growth, and traditional single-server approaches often struggle to meet the demand for large-scale data processing and computation. The Big Data AI Service Network, through a cluster of distributed servers, can flexibly adjust resources, achieve high availability and fault tolerance, and expand resources based on changing business needs, thus meeting the growing demand for big data processing and computation in the digital economy.
4) Drives transformation and value creation
The Big Data AI Service Network promotes data-driven transformation and value creation in the digital economy. Through intelligent data processing and analysis, the ecosystem can gain insights into market demand, optimize resource allocation, and enhance operational efficiency, thus achieving better business development and economic growth. The Big Data AI Service Network also provides opportunities for innovation and growth in various industries, helping companies rapidly develop in emerging fields of the digital economy and driving the prosperity and innovation of the digital economy.
5) Conclusion
In summary, the Big Data AI Service Network, as one of the foundational infrastructures in the digital ecosystem, plays a crucial role in the digital economy. It provides efficient big data storage and computing capabilities, diverse artificial intelligence toolkits, high distribution and scalability, and drives data-driven transformation and value creation in the digital economy.
10.Human-Computer Interaction Infrastructure
a) Concept
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) infrastructure refers to the collection of technologies, tools, and systems within a digital ecosystem that support interactions between humans and computers or other digital entities. It includes hardware and software technologies, standards, and protocols used for interface design, interaction methods, and user experience, as well as various technologies and tools that facilitate information exchange, command input, and output of results between users and computer systems. The goal of HCI infrastructure is to provide intuitive, efficient, and user-friendly interfaces that enable human users to effectively communicate and interact with computer systems, thus achieving a more intelligent, convenient, and personalized computing experience.
b) Functions
HCI infrastructure includes, but is not limited to, mobile apps, mini-programs, PCs, motion-sensing devices, digital twins, XR (virtual reality/augmented reality), smart terminals, brain-computer interfaces, etc. The following are the important functions of HCI infrastructure as one of the foundational infrastructures in the digital economy:
1) Improving User Experience
HCI infrastructure improves the interaction experience between users and computer systems by providing intuitive, efficient, and user-friendly interfaces and interaction methods. Optimized user interface design and interaction methods can reduce users' learning costs and usage difficulties, and increase user satisfaction and loyalty, thereby encouraging more users to actively participate in services and platforms in the digital economy.
2) Promoting Functional Innovation of Digital Services and Platforms
The continuous innovation and development of HCI infrastructure drive functional innovation and experience upgrades of digital services and platforms. The introduction of new interaction methods and experiences such as intelligent voice assistants, virtual reality, augmented reality, and others, constantly expands the ways users interact with the digital world, providing more intelligent, convenient, and personalized computing experiences. As a result, digital services and platforms in the digital economy constantly introduce new features and services to meet the growing needs of users.
3) Facilitating Interoperability and Connectivity of Digital Services and Platforms
HCI infrastructure enables compatibility and interoperability among different systems through the application of standards and protocols, promoting seamless connections and data exchange between digital services and platforms. This creates conditions for cross-system collaboration and sharing in the digital economy, facilitating the integration and coordinated development of the digital economic ecosystem.
4) Providing Intelligent and Personalized Computing Experience
HCI infrastructure continuously incorporates intelligent technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to recognize and adapt to users' personalized needs and behaviors, thus providing intelligent and personalized computing experiences. This helps improve user satisfaction and loyalty, encouraging users to use digital services and platforms more frequently, and driving the development of the digital economy.
5) Promoting Digital Ecological Innovation and Development
As one of the foundational infrastructures of the digital ecological system, HCI infrastructure promotes digital ecological innovation and development. By continuously introducing new HCI methods and technologies, such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and brain-computer interfaces, HCI infrastructure drives the emergence of innovative applications and business models in the digital economy. These new HCI methods and technologies bring about entirely new user experiences and business opportunities, stimulating the vitality of various innovative enterprises in the digital ecosystem and promoting the sustained development of the digital economy.
6) Enhancing Digital Ecological Security and Privacy Protection
HCI infrastructure plays a critical role in the digital economy, involving sensitive data such as personal information and interaction behaviors of participants. Therefore, the security and privacy protection of HCI infrastructure are of paramount importance. By integrating digital identity networks and adopting advanced security measures such as identity authentication, data encryption, and user permission management, HCI infrastructure helps enhance the security and privacy protection level of the digital ecosystem, safeguarding the legitimate rights and interests of users and maintaining the sustainable and healthy development of the digital economy.
7) Promoting Inclusive Development of the Digital Economy
The development of HCI infrastructure promotes the inclusive development of the digital economy, enabling more people to participate in digital services and platforms and enjoy the convenience and benefits of the digital economy. By providing diverse HCI methods such as voice recognition, gesture recognition, brain-computer interfaces, etc., HCI infrastructure lowers the barriers to entry for participating in the digital economy, making it easier for more users to use digital services and platforms. This in turn promotes the inclusive development of the digital economy and reduces the digital divide.
8) Conclusion
In summary, as one of the foundational infrastructures of the digital ecosystem, HCI infrastructure plays a crucial role in the development of the digital economy. It contributes positively to the improvement of user experience, the promotion of functional innovation of digital services and platforms, the interconnection of digital services and platforms, the provision of intelligent and personalized computing experiences, the promotion of digital ecosystem innovation and development, the enhancement of digital ecological security and privacy protection, and the promotion of inclusive development of the digital economy.
C. The Role and Importance of Soft Infrastructure in the Digital Ecosystem
Soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem plays a crucial role and its importance is reflected in the following aspects:
1.Ensuring the basic operation of the digital economy
oft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem, including digital identity networks, consensus-based regulatory networks, social networks, financial transaction and payment networks, cross-platform API service networks, open source contribution networks, data element circulation networks, big data and AI service networks, and human-computer interaction infrastructure, provides guarantees for the basic operation of the digital economy. By providing stable, efficient, and secure networks and services, it ensures the normal operation of the digital economy and promotes its self-optimization and evolution.
2.Achieving the goals of "three public" and "six common"
Soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem provides the foundation for achieving goals such as fairness, justice, openness, co-building, co-sharing, co-existence, and win-win. By establishing mechanisms such as digital identity networks and consensus-based regulatory networks, it promotes social integrity, addresses issues such as chaotic competition and unfair competition in capital, and promotes distribution based on labor, demand, and common prosperity, thus realizing a fair, just, and transparent digital economic environment.
3.Driving digital transformation and innovative development
Soft infrastructure as a critical component of the digital ecosystem supports digital transformation and innovative development. Through cross-platform API service networks, big data and AI service networks, it provides open technology and data resources for enterprises and innovators, promotes innovation and development of the digital economy, and accelerates the process of digital transformation.
4.Promoting interconnectivity of digital services and platforms
The soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem enables interconnectivity of various services and platforms through digital identity networks, consensus-based regulatory networks, social networks, financial transaction payment networks, cross-platform API service networks, etc. This promotes resource sharing, collaborative innovation, and cross-industry cooperation within the digital ecosystem.
5.Improving user experience and providing intelligent services
The soft infrastructure, through human-machine interaction infrastructure, social networks, etc., provides diverse user interfaces, interaction methods, and intelligent services, thereby improving user experience, meeting personalized user demands, and enhancing user stickiness and engagement in the digital economy.
6.Promoting innovation and development in the digital ecosystem
As the innovation foundation of the digital ecosystem, the soft infrastructure promotes the vitality and innovation development of various innovative enterprises in the digital ecosystem through open-source collaborative contribution networks, data element circulation networks, etc., facilitating the continuous growth and sustainable development of the digital economy.
7.Enhancing digital ecosystem security and privacy protection
The soft infrastructure, through digital identity networks, consensus-based regulatory networks, etc., strengthens the security and privacy protection of the digital ecosystem, safeguarding the personal information and interaction behavior data of participants, and ensuring the robustness and trustworthiness of the digital economic ecosystem.
8.Promoting inclusive development of the digital economy
The development of soft infrastructure has lowered the barriers for participation in the digital economy, making it easier for more people to access digital services and platforms, promoting inclusive development of the digital economy, achieving widespread coverage of digital services, and driving a more inclusive and sustainable development of the digital economy.
9.Promoting digital ecosystem governance and win-win cooperation
The soft infrastructure, through consensus-based regulatory networks, open-source collaborative contribution networks, etc., promotes standardized governance and multi-party cooperation in the digital ecosystem, fostering win-win cooperation among all parties within the digital ecosystem, and achieving sustained and healthy development of the digital economic ecosystem.
10.Conclusion
In summary, soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem plays an irreplaceable role in promoting the development of the digital economy, fostering innovation and collaborative cooperation, enhancing user experience and security protection, etc. Soft infrastructure provides the network foundation for interconnectivity in the digital ecosystem, promoting integration and interaction of digital services and platforms, improving user experience and engagement, and driving inclusive and sustainable development of the digital economy. Furthermore, soft infrastructure strengthens the security and privacy protection of the digital ecosystem, promotes standardized governance and win-win cooperation in the digital ecosystem, and creates a favorable environment for the healthy development of the digital ecosystem.
VII. Challenges and Prospects of the Digital Ecosystem
A. Challenges and Issues Faced by the Digital Ecosystem
As a complex system, the digital ecosystem faces diverse challenges and issues, including but not limited to the following:
1.Data security and privacy protection
The digital ecosystem involves the flow and sharing of a large amount of data, including sensitive information such as users' personal information and businesses' commercial data. However, the soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem faces challenges in data storage, transmission, and processing in terms of security and privacy protection. Risks such as data breaches, data misuse, and cyber attacks may have negative impacts on the stable operation of the digital ecosystem and user trust.
2.Fair competition and regulatory compliance
The digital ecosystem has seen the emergence of numerous digital enterprises and innovative projects. However, due to low market entry barriers and lagging regulatory policies, issues such as unfair competition and disorderly competition of capital may arise. In addition, mechanisms such as consensus-based regulatory networks in the digital ecosystem are still in the exploratory and construction phase, posing difficulties and challenges in regulatory compliance.
3.Technical Standards and Interoperability
In the digital ecosystem, there are multiple software infrastructures involved, but inconsistent technical standards and poor interoperability between different platforms and systems can lead to information silos and hinder the circulation and collaborative development of the digital economy, especially when the digital ecosystem grows to a massive scale.
4.Social Credit and Trust Building
Effective trust mechanisms need to be established in the software infrastructure of the digital ecosystem to ensure that individuals, governments, and businesses can rely on and trust the behaviors of all parties in the process of digital economic interactions. However, issues related to social credit still exist, including false information, online fraud, intellectual property infringement, and other phenomena, which may have adverse effects on the normal operation of the digital ecosystem and user trust.
5.Hardware Infrastructure and Digital Divide
The software infrastructure of the digital ecosystem relies on the support of hardware infrastructure, including computing devices, communication networks, and so on. However, there are still gaps in the construction and popularization of hardware infrastructure in some regions and countries, leading to a digital divide that restricts the comprehensive development and popularization of the digital ecosystem.
6.Innovation and Talent Cultivation
The digital ecosystem presents new requirements for technological innovation and talent cultivation. However, technological innovation in the field of the digital economy is rapidly developing, and there is a demand for high-level technical talents. But the construction and operation of the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem require interdisciplinary knowledge and comprehensive abilities involving multiple fields such as computer science, network security, and data management. Therefore, there may be a shortage of talent and insufficient talent cultivation in the digital ecosystem, which affects the sustainable development and optimization of the digital ecosystem.
7.Fairness, Justice, and Social Inclusiveness
The development of the digital ecosystem should pursue fairness, justice, and social inclusiveness, ensuring that the opportunities and benefits of the digital economy can be widely shared among various social groups. However, due to information asymmetry and the digital divide in the construction and use of software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem, some social groups may be at a disadvantage in the digital economy, which may affect the fairness, justice, and social inclusiveness of the digital ecosystem.
8.Laws, Regulations, and Policy Environment
The development of the digital ecosystem requires a sound legal framework and policy environment to ensure the compliant operation and risk management of the digital economy. However, the software infrastructure in the digital ecosystem involves multiple areas, such as digital identity networks, financial transaction payment networks, etc., and relevant laws, regulations, and policy environment may be relatively lagging or incomplete, leading to legal risks and policy uncertainties in the digital ecosystem.
9.Sustainable Development and Environmental Impacts
The development of the digital ecosystem should consider sustainable development and environmental impacts, including energy consumption of digital infrastructure, electronic waste disposal, and other issues. In the digital ecosystem, the large-scale operation of software infrastructure may have certain impacts on energy resources and the environment, and measures need to be taken to ensure the sustainable development and environmental friendliness of the digital ecosystem.
10.Conclusion
In summary, the digital ecosystem faces many challenges and issues, including data security and privacy protection, fair competition and regulatory compliance, technical standards and interoperability, social integrity and trust-building, hardware infrastructure and digital divide, innovation and talent cultivation, fairness, justice, and social inclusiveness, laws, regulations, and policy environment, sustainable development and environmental impacts, etc. Addressing these issues requires joint efforts from various stakeholders, including government, enterprises, academia, social organizations, and individuals, to promote the healthy development of the digital ecosystem.
B. Strategies for Addressing Challenges and Issues
In addressing the challenges and issues faced by the digital ecosystem, it is important to follow the approach of building a comprehensive digital ecosystem system. Many problems can be effectively addressed with this approach, but constant vigilance is required to ensure that the digital ecosystem develops and evolves towards its common goals. In addition to building soft infrastructure, the following potential strategies can be adopted:
1.Data security and privacy protection
Establish a robust legal and regulatory framework for data security and privacy protection, enhance research and innovation in data security technologies, and improve the technical capabilities and management level of data security and privacy protection. At the same time, strengthen user education, raise awareness of data security and privacy protection among users, and encourage users to independently manage and control their personal data.
2.Fair competition and regulatory compliance
Establish a level playing field in the market environment to ensure fair competition, strengthen the regulatory and compliance management of enterprises in the digital ecosystem, and prevent monopolistic behaviors and unfair competition practices. Meanwhile, enhance the regulatory capabilities and technological applications of regulatory agencies, and promote innovation and collaboration in digital economy regulation.
3.Technology standards and interoperability
Promote the development and adoption of technology standards, facilitate interoperability among different components of the digital ecosystem, reduce technological barriers within the digital ecosystem, and promote the sharing and interconnectivity of digital resources.
4.Social Credit and Trust Building
Advocate for a digital culture that promotes integrity and trust, strengthen the protection of rights and interests of all participants, and promote the establishment and maintenance of trust relationships in the digital ecosystem. At the same time, enhance self-discipline and supervision of social organizations and industry associations, and promote the implementation of credit and trust building in the digital ecosystem.
5.Hardware Infrastructure and Digital Divide
Increase investment and construction of digital infrastructure, especially in areas with a large digital divide and low population density, promote the popularization and coverage of hardware infrastructure, narrow the digital divide, and ensure inclusiveness and accessibility in the digital ecosystem.
6.Innovation and Talent Development
Strengthen innovation research and development in the digital ecosystem, promote technology transfer and application, and foster technological innovation and business model innovation in the digital ecosystem. At the same time, enhance talent development and recruitment, improve the talent reserves and quality in the digital ecosystem, and meet the needs of digital economic development.
7.Fairness, Justice, and Social Inclusiveness
Promote fairness, justice, and social inclusiveness in the digital ecosystem, focus on protecting the rights and interests of vulnerable groups, prevent information asymmetry, digital divide, and digital exclusion in the digital ecosystem. Strengthen digital education and training, improve the digital literacy of the general public, and ensure that more people can participate in and share the development achievements of the digital ecosystem.
8.International Cooperation and Cross-border Governance
Strengthen international cooperation, promote compliant and secure cross-border data flow, and promote international interconnection and win-win cooperation in the digital ecosystem. Strengthen compliance management of transnational enterprises, comply with local laws, regulations, and cultural customs, and promote the sustainable development of the digital ecosystem in different countries and regions.
9.Environmental Sustainability
The consumption of energy, resources, and the environment by the digital ecosystem is also an important issue. In the development process of the digital ecosystem, attention should be paid to environmental sustainability, promote the green development of digital technologies, reduce the negative impact of the digital ecosystem on the environment, including reducing the energy consumption and carbon emissions of digital infrastructure, and improving the environmental performance of digital products and services.
10.Conclusion
The above are only part of the challenges and issues faced by the digital ecosystem, and solving these challenges and issues requires multi-party cooperation, including government, enterprises, academia, social organizations, and individual users, to jointly participate. Only through collaborative construction, sharing, and governance, can the digital ecosystem develop in a healthy manner, better utilize digital technologies to promote economic and social development, and achieve sustainable development goals in the digital era.
C. Trends and Prospects for the Future Development of Digital Ecosystem
The future development of the digital ecosystem will be influenced by various factors, including technology, economy, society, and policy. The following are some possible trends and prospects:
1.Comprehensive Popularization of Digitalization
In the future, the digital ecosystem will witness a trend of comprehensive popularization of digitalization, where digital technologies, including artificial intelligence, big data, Internet of Things, blockchain, etc., will be widely applied in various fields. Digital technologies will be embedded in all aspects of economy, society, and life, driving industrial upgrading and economic growth, improving productivity and efficiency.
2.Cross-industry Integration and Innovative Applications
In the future, the digital ecosystem will promote the integration and innovative applications across different industries and fields. Digital technologies will generate new industrial and business models, accelerate the digital transformation of various industries, promote the integration of traditional industries with the digital economy, and create new value and employment opportunities.
3.Data-driven and Intelligent Development
In the future, the digital ecosystem will pay more attention to data-driven and intelligent development. Big data and artificial intelligence will become the core driving forces of the digital economy, promoting intelligence and optimization in various aspects of the digital ecosystem through data collection, analysis, and application, enhancing user experience and social benefits.
4.Security and Privacy Protection
The future digital ecosystem will face more complex and severe challenges in security and privacy protection. With the rapid development of digital technologies, cybersecurity threats are increasing, and the risks of personal information and data privacy breaches are rising. The future digital ecosystem needs to strengthen the research and application of security technologies and privacy protection mechanisms to ensure the robust and sustainable development of the digital economy.
5.Social Equity and Inclusiveness
In the future digital ecosystem, there will be increased focus on social equity and inclusiveness, with a commitment to protecting the rights and opportunities of vulnerable groups. Digital technologies should serve all people and not exacerbate the digital divide and social exclusion. The future digital ecosystem needs to promote fair and just digital economic development, and strive towards the goal of co-building and sharing.
6.International Cooperation and Cross-border Governance
In the future digital ecosystem, there will be a need to strengthen international cooperation and cross-border governance, promoting international connectivity and win-win cooperation in the digital economy. The digital era is characterized by cross-border and global nature, and the development of the digital ecosystem requires cross-national and cross-regional cooperation and governance, including data flow, cross-border internet business, standards, and norms. The future digital ecosystem needs to establish international cooperation mechanisms to promote interconnectedness and common prosperity in the digital economy.
7.Innovation and Entrepreneurship Ecosystem
In the future digital ecosystem, there will be efforts to promote the development of innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystem. The digital economy will become a driving force for innovation, encouraging innovators and entrepreneurs to conduct innovative activities within the digital ecosystem, promoting continuous innovation in technology, products, and business models. Governments, businesses, and society should jointly build an ecosystem for innovation and entrepreneurship, supporting the development of innovative companies and startups.
8.Smart Cities and Digital Society
In the future digital ecosystem, there will be efforts to promote the development of smart cities and digital society. Digital technologies will be applied in urban management, public services, social governance, and other areas, promoting the intelligence and digitization transformation of cities. Digital society will foster new models of social interaction in areas such as socializing, education, healthcare, culture, and change people's lifestyles and ways of socializing.
9.Conclusion
In summary, the future digital ecosystem will witness rapid development in technology, economy, society, and policies. Digital technologies will be widely applied in various industries, and the digital economy will become a new engine for economic growth and social development. However, the digital ecosystem also faces many challenges and issues, including security, privacy, social equity, and international cooperation, which require joint efforts from all parties to promote healthy, sustainable, inclusive, and innovative development of the digital economy. The future digital ecosystem is expected to bring new opportunities and vitality to economic and social development, and bring more convenience and value to people's lives and work. Let us move towards the vision of a world of unity, harmony, and coexistence.
VIII. Conclusion and Recommendations
A. Research Conclusions and Findings
The digital ecosystem is a crucial support for the development of the digital economy, with soft infrastructure playing a key role within it. Through the analysis of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem, the following conclusions and findings can be drawn:
1.Soft infrastructure plays a significant role in the digital ecosystem
Soft infrastructure includes digital identity networks, consensus-based regulatory networks, social (community, society) networks, financial transaction and payment networks, cross-platform API service networks, open-source contribution networks, data element circulation networks, big data AI service networks, human-computer interaction infrastructure, etc. These provide the basic guarantees for the smooth operation and optimized evolution of the digital economy within the digital ecosystem. The soundness and improvement of soft infrastructure are of great significance to the development of the digital ecosystem and the sustained growth of the digital economy.
2.Soft infrastructure achieves the goals of "three publics" and "six shared"
The construction and development of soft infrastructure contribute to the principles of fairness, justice, transparency, and co-construction and sharing within the digital ecosystem. For example, digital identity networks can ensure the legitimacy of digital economy participants and the protection of their rights and interests; consensus-based regulatory networks can achieve effective regulation and governance of the digital economy; social networks can promote interaction and collaboration among digital economy participants; financial transaction and payment networks can ensure the security and convenience of transactions in the digital economy; cross-platform API service networks can facilitate interconnection and collaboration among digital economy participants; open-source contribution networks can drive innovation and development in the digital economy; data element circulation networks can facilitate the circulation and sharing of data elements in the digital economy; big data AI service networks can provide data processing and intelligent services for digital economy participants; and human-computer interaction infrastructure can improve the user experience and interaction methods of digital economy participants.
3.Soft infrastructure solves many problems in the digital ecosystem
The construction and development of soft infrastructure helps to address issues in the digital ecosystem such as trustworthiness, disorderly competition in capital, unfair competition, as well as labor-based distribution, demand-based distribution, and common prosperity. For example, digital identity networks can enhance the credibility and trustworthiness of participants in the digital economy; consensus-based regulatory networks can strengthen the regulation and governance of the digital economy, preventing unfair competition and disorderly competition in capital; social networks can promote trust and cooperation among participants in the digital economy, preventing information fraud and scams; financial transaction and payment networks can ensure the security of funds and convenient transactions in the digital economy; cross-platform API service networks can facilitate cooperation and resource sharing among participants in the digital economy; open-source collaborative contribution networks can drive innovation and mutual development in the digital economy; data element circulation networks can facilitate the flow and sharing of data in the digital economy, enhancing the value and efficiency of data utilization; big data AI service networks can provide more intelligent services and decision support for participants in the digital economy; human-machine interaction infrastructure can improve the user experience of participants in the digital economy and promote the popularization of digital skills.
4.Conclusion
In conclusion, soft infrastructure for the digital economy plays a crucial role in its development. The future development trends will include globalization, interconnectivity, security and reliability, data governance and privacy protection, innovation-driven development, as well as user experience and human-machine interaction. Governments, enterprises, and all stakeholders in society should strengthen cooperation and jointly promote the development of soft infrastructure for the digital economy to promote robust development and improve the quality and efficiency of the digital economy.
B. Recommendations for the Construction of Digital Ecological System
This paper has studied the role and importance of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system, elaborated on the challenges and issues faced by the digital ecological system, as well as the future development trends and prospects. Based on the research findings, the following recommendations are proposed for the construction of the digital ecological system:
1.Strengthen the construction of digital economy soft infrastructure
The soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system is an important foundation for supporting the operation and development of the digital economy. Efforts should be made to strengthen the construction of digital identity networks, consensus-based governance networks, social networks, financial transaction and payment networks, cross-platform API service networks, open-source contribution networks, data element circulation networks, big data and AI service networks, and human-machine interaction infrastructure, etc., to provide stable, secure, and efficient services.
2.Promote global interconnection and interoperability
The digital economy has become a trend of globalization, and the soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system should support global interconnection and interoperability, including capabilities such as cross-border payment, cross-border data transmission, and cross-border compliance, to promote cross-border cooperation and communication among digital economy participants.
3.Enhance innovation-driven by science and technology
The development of the digital economy relies on technological innovation. The soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system should continuously promote the application of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, etc., to improve the technological level and functionality of digital economy soft infrastructure.
4.Strengthen data governance and privacy protection
The large amount of data generated by the digital economy requires effective data governance and privacy protection mechanisms. The soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system should establish a sound system for data management, data security, and privacy protection, in order to safeguard the data security and privacy rights of digital economy participants.
5.Focus on user experience and human-machine interaction
The soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system should pay attention to user needs and provide convenient, user-friendly, and intelligent interfaces, interaction methods, and personalized services, in order to improve the satisfaction and user experience of digital economy participants.
6.Conclusion
Through the above recommendations, the healthy development of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system can be promoted, the digital economy can be vigorously developed, and the quality and efficiency of the digital economy can be enhanced.
D. Limitations of the research and further research directions
In this paper, although a detailed study has been conducted on the role, challenges, trends, and recommendations of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system, mainly from the perspectives of concepts and methods, there are still some limitations. Further research can be conducted in the following areas:
1.In-depth study of technological innovation and application of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system
This paper mainly focuses on the role and development trends of soft infrastructure in the digital economy, but lacks in-depth exploration of the application scenarios, technical architecture, and effectiveness evaluation of different technologies in soft infrastructure. Future research can delve into the innovative applications of different technologies in the digital ecological system, such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, big data, etc., and explore their impacts and driving forces on the digital economy. In-depth research and discussion on each soft infrastructure system can be conducted.
2.In-depth study of security and privacy protection of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system
The large amount of data and information generated by the digital economy involves issues of security and privacy. Although this paper mentions data governance and privacy protection in the recommendations, it lacks in-depth exploration of the security risks and privacy protection mechanisms of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system. Future research can conduct in-depth research on the security and privacy protection of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system, and explore effective security and privacy protection strategies.
3.In-depth study of globalization and interconnectivity of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system
This paper mentions the globalization trend of the digital economy and the globalization and interconnectivity of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system, but lacks in-depth exploration of the mechanisms, policies, and practices of globalization and interconnectivity. Future research can conduct in-depth research on the globalization and interconnectivity of soft infrastructure in the digital ecological system, including mechanisms and practices related to cross-border payments, cross-border data transmission, cross-border compliance, and other aspects.
4.In-depth study of the socio-economic effects of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem
This paper mainly focuses on the supportive role of soft infrastructure in the digital economy, but does not delve into its impact on socio-economic development. Future research can delve into the socio-economic effects of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem, including in-depth studies on employment, economic growth, industrial upgrading, and social inclusion.
5.In-depth study of the policy and governance of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem
The construction of the digital ecosystem requires policy and governance support and guidance. Although the importance of policy support is mentioned in the recommendations of this paper, the policies and governance mechanisms of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem are not deeply explored. Future research can conduct in-depth studies on the policy formulation, implementation, and effectiveness evaluation of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem, including consensus mechanisms and co-governance mechanisms.
6.In-depth study of the sustainable development of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem
The sustainable development of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem is an important issue, including resource utilization efficiency, environmental protection, and social responsibility. This paper did not delve into the sustainable development issues of soft infrastructure. Future research can conduct in-depth studies on the sustainability of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem from the perspective of sustainable development, including research on green technology application, resource recycling, and social responsibility.
7.In-depth study of the evaluation and full life cycle management of data elements in the digital ecosystem
Data elements in the digital ecosystem play important roles throughout their life cycle, including data generation, collection, rights confirmation, storage, evaluation, transaction, processing, transmission, analysis, and application stages. For the construction and operation of the digital ecosystem, the evaluation and full life cycle management of data elements are crucial. This paper did not delve into this issue, and future research can conduct in-depth studies on the full life cycle management of data elements.
8.In-depth study of the quantification and allocation of contributions from participants in the digital ecosystem
Participants in the digital ecosystem include various stakeholders such as companies, governments, social organizations, and individuals, who contribute different resources and values to the digital ecosystem. Therefore, in-depth research on the quantification and allocation of contributions from participants in the digital ecosystem is of great significance for fair distribution and sharing of benefits in the digital ecosystem. This paper did not delve into this issue, and future research can conduct in-depth studies from multiple aspects, such as quantification indicators of participant contributions, allocation mechanisms of participant contributions, dynamic changes and adjustments of participant contributions, and multidimensional analysis of participant contributions.
9.Conclusion
In summary, although this paper has conducted in-depth research on the roles, challenges, trends, and recommendations of soft infrastructure in the digital ecosystem, there are still shortcomings as mentioned above. Future research can delve into these aspects to better promote the construction and development of the digital ecosystem.
IX. References
A. Core Intellectual Property Rights Belong to the Authors
The core ideas, core values, basic framework, core methods, and other intellectual property rights of this article belong solely to the authors. The content related to the "ecosystem architecture and methods supporting the sustainable operation of the digital economy" is being filed for patent application. Please respect the originality and do not infringe on the rights of the authors.
B. Other Sources of Content
Other content such as references, structural design, language organization, translation, proofreading, etc., were assisted by ChatGPT.
C. Image Sources
Architecture diagram: Original creation by the authors.
Illustrations: Created using AI (Powered by Bing Image Creator).

扫码关注我们